Semaphorins and their Signaling Mechanisms
- PMID: 27787839
- PMCID: PMC5538787
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6448-2_1
Semaphorins and their Signaling Mechanisms
Abstract
Semaphorins are extracellular signaling proteins that are essential for the development and maintenance of many organs and tissues. The more than 20-member semaphorin protein family includes secreted, transmembrane and cell surface-attached proteins with diverse structures, each characterized by a single cysteine-rich extracellular sema domain, the defining feature of the family. Early studies revealed that semaphorins function as axon guidance molecules, but it is now understood that semaphorins are key regulators of morphology and motility in many different cell types including those that make up the nervous, cardiovascular, immune, endocrine, hepatic, renal, reproductive, respiratory and musculoskeletal systems, as well as in cancer cells. Semaphorin signaling occurs predominantly through Plexin receptors and results in changes to the cytoskeletal and adhesive machinery that regulate cellular morphology. While much remains to be learned about the mechanisms underlying the effects of semaphorins, exciting work has begun to reveal how semaphorin signaling is fine-tuned through different receptor complexes and other mechanisms to achieve specific outcomes in various cellular contexts and physiological systems. These and future studies will lead to a more complete understanding of semaphorin-mediated development and to a greater understanding of how these proteins function in human disease.
Keywords: Axon guidance; Cell morphology; Cellular guidance; Inhibition; Motility; Navigation; Neuropilin; Plexin; Repulsive signaling; Semaphorin; Signaling to the cytoskeleton.
Figures
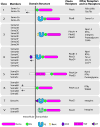
References
-
- Kolodkin AL, Matthes DJ, Goodman CS. The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmembrane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules. Cell. 1993;75:1389–1399. - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin AL, Matthes DJ, O’Connor TP, et al. Fasciclin IV: sequence, expression, and function during growth cone guidance in the grasshopper embryo. Neuron. 1992;9:831–845. - PubMed
-
- Raper JA, Kapfhammer JP. The enrichment of a neuronal growth cone collapsing activity from embryonic chick brain. Neuron. 1990;4:21–29. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y, Raible D, Raper JA. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993;75:217–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

