Data-driven approaches used for compound library design, hit triage and bioactivity modeling in high-throughput screening
- PMID: 27789427
- PMCID: PMC6018726
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbw105
Data-driven approaches used for compound library design, hit triage and bioactivity modeling in high-throughput screening
Abstract
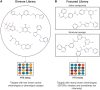
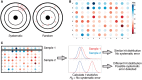
High-throughput screening (HTS) campaigns are routinely performed in pharmaceutical companies to explore activity profiles of chemical libraries for the identification of promising candidates for further investigation. With the aim of improving hit rates in these campaigns, data-driven approaches have been used to design relevant compound screening collections, enable effective hit triage and perform activity modeling for compound prioritization. Remarkable progress has been made in the activity modeling area since the recent introduction of large-scale bioactivity-based compound similarity metrics. This is evidenced by increased hit rates in iterative screening strategies and novel insights into compound mode of action obtained through activity modeling. Here, we provide an overview of the developments in data-driven approaches, elaborate on novel activity modeling techniques and screening paradigms explored and outline their significance in HTS.
Figures

References
-
- Drews J. Drug discovery: a historical perspective. Science 2000;287:1960–4. - PubMed
-
- Macarron R. Critical review of the role of HTS in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 2006;11:277–9. - PubMed
-
- Paricharak S, IJzerman AP, Bender A, et al. Analysis of iterative screening with stepwise compound selection based on Novartis in-house HTS data. ACS Chem Biol 2016;11:1255–64. - PubMed
-
- Mayr LM, Fuerst P.. The future of high-throughput screening. J Biomol Screen 2008;13:443–8. - PubMed
-
- Mayr LM, Bojanic D.. Novel trends in high-throughput screening. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2009;9:580–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

