Mouse-based genetic modeling and analysis of Down syndrome
- PMID: 27789459
- PMCID: PMC5146682
- DOI: 10.1093/bmb/ldw040
Mouse-based genetic modeling and analysis of Down syndrome
Abstract
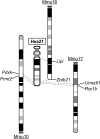
Introduction: Down syndrome (DS), caused by human trisomy 21 (Ts21), can be considered as a prototypical model for understanding the effects of chromosomal aneuploidies in other diseases. Human chromosome 21 (Hsa21) is syntenically conserved with three regions in the mouse genome.
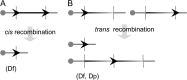
Sources of data: A review of recent advances in genetic modeling and analysis of DS. Using Cre/loxP-mediated chromosome engineering, a substantial number of new mouse models of DS have recently been generated, which facilitates better understanding of disease mechanisms in DS.
Areas of agreement: Based on evolutionary conservation, Ts21 can be modeled by engineered triplication of Hsa21 syntenic regions in mice. The validity of the models is supported by the exhibition of DS-related phenotypes.
Areas of controversy: Although substantial progress has been made, it remains a challenge to unravel the relative importance of specific candidate genes and molecular mechanisms underlying the various clinical phenotypes.
Growing points: Further understanding of mechanisms based on data from mouse models, in parallel with human studies, may lead to novel therapies for clinical manifestations of Ts21 and insights to the roles of aneuploidies in other developmental disorders and cancers.
Keywords: Down syndrome; chromosome engineering; human trisomy 21; mouse models.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Parker SE, Mai CT, Canfield MA, et al. . Updated National Birth Prevalence estimates for selected birth defects in the United States, 2004–2006. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 2010;88:1008–16. - PubMed
-
- Natoli JL, Ackerman DL, McDermott S et al. . Prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome: a systematic review of termination rates (1995–2011). Prenat Diagn 2012;32:142–53. - PubMed
-
- LeJeune J, Gautier M, Turpin R. Etudes des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. Comptes Renus de l’ Academic les Sciences 1959;248:1721–2. - PubMed
-
- LeJeune J, Turpin R, Gautier M. Le mongolism: premier éxample d'aberration autosomique humaine. Ann Genet 1959;1:41–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

