Role of FAST Kinase Domains 3 (FASTKD3) in Post-transcriptional Regulation of Mitochondrial Gene Expression
- PMID: 27789713
- PMCID: PMC5207062
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.730291
Role of FAST Kinase Domains 3 (FASTKD3) in Post-transcriptional Regulation of Mitochondrial Gene Expression
Abstract
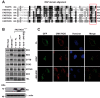
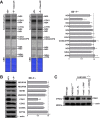
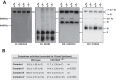
The Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (FASTK) family of proteins has recently emerged as a central regulator of mitochondrial gene expression through the function of an unusual RNA-binding domain named RAP (for RNA-binding domain abundant in Apicomplexans), shared by all six members of the family. Here we describe the role of one of the less characterized members, FASTKD3, in mitochondrial RNA metabolism. First, we show that, in contrast to FASTK, FASTKD2, and FASTKD5, FASTKD3 does not localize in mitochondrial RNA granules, which are sites of processing and maturation of mtRNAs and ribosome biogenesis. Second, we generated FASTKD3 homozygous knock-out cell lines by homologous recombination and observed that the absence of FASTKD3 resulted in increased steady-state levels and half-lives of a subset of mature mitochondrial mRNAs: ND2, ND3, CYTB, COX2, and ATP8/6. No aberrant processing of RNA precursors was observed. Rescue experiments demonstrated that RAP domain is required for FASTKD3 function in mRNA stability. Besides, we describe that FASTKD3 is required for efficient COX1 mRNA translation without altering mRNA levels, which results in a decrease in the steady-state levels of COX1 protein. This finding is associated with reduced mitochondrial complex IV assembly and activity. Our observations suggest that the function of this family of proteins goes beyond RNA processing and ribosome assembly and includes RNA stability and translation regulation within mitochondria.
Keywords: FASTKD3; RNA; RNA metabolism; gene expression; mitochondria; post-transcriptional regulation; translation; translation control.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The FASTK family of proteins: emerging regulators of mitochondrial RNA biology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 2;45(19):10941-10947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx772. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29036396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Analysis of FASTK Gene Family Alterations in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 20;22(21):11337. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111337. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768773 Free PMC article.
-
FASTKD2 is an RNA-binding protein required for mitochondrial RNA processing and translation.RNA. 2015 Nov;21(11):1873-84. doi: 10.1261/rna.052365.115. Epub 2015 Sep 14. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26370583 Free PMC article.
-
FASTKD1 and FASTKD4 have opposite effects on expression of specific mitochondrial RNAs, depending upon their endonuclease-like RAP domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 2;45(10):6135-6146. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx164. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28335001 Free PMC article.
-
A concert of RNA-binding proteins coordinates mitochondrial function.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Dec;53(6):652-666. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2018.1553927. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30741581 Review.
Cited by
-
The FASTK family of proteins: emerging regulators of mitochondrial RNA biology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 2;45(19):10941-10947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx772. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29036396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of gene expression patterns in mild cognitive impairment using a transcriptomics approach and neuroimaging endophenotypes.Alzheimers Dement. 2022 Dec;18(12):2493-2508. doi: 10.1002/alz.12587. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Alzheimers Dement. 2022. PMID: 35142026 Free PMC article.
-
How RNases Shape Mitochondrial Transcriptomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 30;23(11):6141. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116141. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and phylogenetic analysis of RNA binding domain abundant in apicomplexans or RAP proteins.Microb Genom. 2021 Mar;7(3):mgen000541. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000541. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 33656416 Free PMC article.
-
The FASTK family proteins fine-tune mitochondrial RNA processing.PLoS Genet. 2021 Nov 8;17(11):e1009873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009873. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34748562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ojala D., Montoya J., and Attardi G. (1981) tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 290, 470–474 - PubMed
-
- Xu F., Ackerley C., Maj M. C., Addis J. B., Levandovskiy V., Lee J., Mackay N., Cameron J. M., and Robinson B. H. (2008) Disruption of a mitochondrial RNA-binding protein gene results in decreased cytochrome b expression and a marked reduction in ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase activity in mouse heart mitochondria. Biochem. J. 416, 15–26 - PubMed
-
- Simarro M., Gimenez-Cassina A., Kedersha N., Lazaro J. B., Adelmant G. O., Marto J. A., Rhee K., Tisdale S., Danial N., Benarafa C., Orduña A., and Anderson P. (2010) Fast kinase domain-containing protein 3 is a mitochondrial protein essential for cellular respiration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 401, 440–446 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baltz A. G., Munschauer M., Schwanhäusser B., Vasile A., Murakawa Y., Schueler M., Youngs N., Penfold-Brown D., Drew K., Milek M., Wyler E., Bonneau R., Selbach M., Dieterich C., and Landthaler M. (2012) The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Mol. Cell 46, 674–690 - PubMed
-
- Castello A., Fischer B., Eichelbaum K., Horos R., Beckmann B. M., Strein C., Davey N. E., Humphreys D. T., Preiss T., Steinmetz L. M., Krijgsveld J., and Hentze M. W. (2012) Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell 149, 1393–1406 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

