18F-5-Fluoroaminosuberic Acid as a Potential Tracer to Gauge Oxidative Stress in Breast Cancer Models
- PMID: 27789715
- PMCID: PMC5331935
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.116.180661
18F-5-Fluoroaminosuberic Acid as a Potential Tracer to Gauge Oxidative Stress in Breast Cancer Models
Abstract
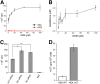
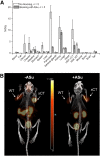
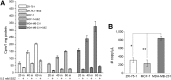
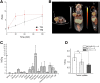
The cystine transporter (system xC-) is an antiporter of cystine and glutamate. It has relatively low basal expression in most tissues and becomes upregulated in cells under oxidative stress (OS) as one of the genes expressed in response to the antioxidant response element promoter. We have developed 18F-5-fluoroaminosuberic acid (FASu), a PET tracer that targets system xC- The goal of this study was to evaluate 18F-FASu as a specific gauge for system xC- activity in vivo and its potential for breast cancer imaging. Methods:18F-FASu specificity toward system xC- was studied by cell inhibition assay, cellular uptake after OS induction with diethyl maleate, with and without anti-xCT small interfering RNA knockdown, in vitro uptake studies, and in vivo uptake in a system xC--transduced xenograft model. In addition, radiotracer uptake was evaluated in 3 breast cancer models: MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, and ZR-75-1. Results: Reactive oxygen species-inducing diethyl maleate increased glutathione levels and 18F-FASu uptake, whereas gene knockdown with anti-xCT small interfering RNA led to decreased tracer uptake. 18F-FASu uptake was robustly inhibited by system xC- inhibitors or substrates, whereas uptake was significantly higher in transduced cells and tumors expressing xCT than in wild-type HEK293T cells and tumors (P < 0.0001 for cells, P = 0.0086 for tumors). 18F-FASu demonstrated tumor uptake in all 3 breast cancer cell lines studied. Among them, triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231, which has the highest xCT messenger RNA level, had the highest tracer uptake (P = 0.0058 when compared with MCF-7; P < 0.0001 when compared with ZR-75-1). Conclusion:18F-FASu as a system xC- substrate is a specific PET tracer for functional monitoring of system xC- and OS imaging. By enabling noninvasive analysis of xC- responses in vivo, this biomarker may serve as a valuable target for the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of certain breast cancers.
Keywords: F-18; PET; oxidative stress; system xC−; tumor imaging.
© 2017 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures
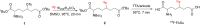
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
