Comparison of rechargeable versus battery-operated insulin pumps: temperature fluctuations
- PMID: 27789976
- PMCID: PMC5072507
- DOI: 10.2147/MDER.S116666
Comparison of rechargeable versus battery-operated insulin pumps: temperature fluctuations
Abstract
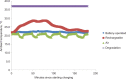
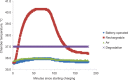
The role of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (insulin pumps) has become increasingly important in diabetes management, and many different types of these systems are currently available. This exploratory study focused on the reported heating issues that lithium-ion battery-powered pumps may have during charging compared with battery-operated pumps. It was found that pump temperature increased by 6.4°C during a long charging cycle of a lithiumion battery-operated pump under ambient temperatures. In an environmental-chamber kept at 35°C, the pump temperature increased by 4.4°C, which indicates that the pump temperature was above that of the recommended safety limit for insulin storage of 37°C. When designing new pumps, and when using currently available rechargeable pumps in warmer climates, the implications of these temperature increases should be taken into consideration. Future studies should also further examine insulin quality after charging.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; heating; insulin pumps; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was sponsored by Animas Corporation. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reported insulin pump temperature fluctuations lack clinical relevance.Med Devices (Auckl). 2017 Feb 20;10:43-46. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S128526. eCollection 2017. Med Devices (Auckl). 2017. PMID: 28260953 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Chen X, Frias JP. Associations between improved glucose control and patient-reported outcomes after initiation of insulin pump therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13(4):471–476. - PubMed
-
- Wen JW, Yu Y, Chen CH. A review on lithium-ion batteries safety issues: existing problems and possible solutions. Mater Express. 2012;2(3):197–212.
-
- Humalog [prescribing information] [Accessed September 20, 2016]. Available from: http://pi.lilly.com/us/humalog-pen-pi.pdf.
-
- NovoLog [prescribing information] [Accessed September 20, 2016]. Available from: http://www.novo-pi.com/novolog.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

