Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 27790009
- PMCID: PMC5045096
- DOI: 10.2147/OARRR.S14723
Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease
Abstract
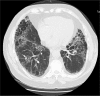
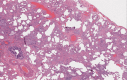
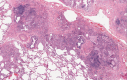
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory disorder affecting 1% of the US population. Patients can have extra-articular manifestations of their disease and the lungs are commonly involved. RA can affect any compartment of the respiratory system and high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the lung is abnormal in over half of these patients. Interstitial lung disease is a dreaded complication of RA. It is more prevalent in smokers, males, and those with high antibody titers. The pathogenesis is unknown but data suggest an environmental insult in the setting of a genetic predisposition. Smoking may play a role in the pathogenesis of disease through citrullination of protein in the lung leading to the development of autoimmunity. Patients usually present in middle age with cough and dyspnea. Pulmonary function testing most commonly shows reduced diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide and HRCT reveals a combination of reticulation and ground glass abnormalities. The most common pattern on HRCT and histopathology is usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), with nonspecific interstitial pneumonia seen less frequently. There are no large-scale well-controlled treatment trials. In severe or progressive cases, treatment usually consists of corticosteroids with or without a cytotoxic agent for 6 months or longer. RA interstitial lung disease is progressive; over half of patients show radiographic progression within 2 years. Patients with a UIP pattern on biopsy have a survival similar to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: anti-CCP; interstitial lung disease; nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; rheumatoid arthritis; usual interstitial pneumonia.
Figures

References
-
- Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1094–1108. - PubMed
-
- van der Woude D, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Toes RE, et al. Quantitative heritability of anti-citrullinated protein antibody-positive and anti-citrullinated protein antibody-negative rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(4):916–923. - PubMed
-
- Carlens C, Hergens MP, Grunewald J, et al. Smoking, use of moist snuff, and risk of chronic inflammatory diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181(11):1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, Reesink HW, et al. Specific autoantibodies precede the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis: a study of serial measurements in blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):380–386. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

