Causative Agents of Onychomycosis: A 7-Year Study
- PMID: 27790797
- PMCID: PMC6807218
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21973
Causative Agents of Onychomycosis: A 7-Year Study
Abstract
Background: Onychomycosis is principally caused by dermatophyte species, but nondermatophyte molds and yeasts have also been involved, causing different clinical manifestations. The aim of this investigation is to determine the clinicomycological and epidemiological profile of the etiologic agents of onychomycosis.
Methods: The study population included 9,785 suspected cases of onychomycosis referred to the Medical Mycology Reference Laboratory in Isfahan, Iran, during 2007-2014. Nail clipping was collected in sterile Petri dishes for direct microscopic examination and culture. Clinical isolates were identified by using phenotypic tests and molecular techniques.
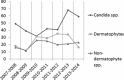
Results: Of total 9,785 cases with clinical suspicion of onychomycosis comprised in the present study, 1,284 patients (13.1%) were positive by direct microscopy. Age range of patients was between 1 and 82 years. Housewives were the commonest infected population. Candida albicans was the most prevalent species isolated from patients in this study (34.9%) followed by Trichophyton interdigitale (11.7%) and Aspergillus flavus (9.1%).
Conclusion: The pattern of causative agents and clinical signs of onychomycosis is altering region to region, so repeated epidemiological surveys of onychomycosis seems to be fundamental. The present study provides novel and appropriate epidemiologic data of onychomycosis for the better prevention and treatment of this fungal infection.
Keywords: causative agents; identification; onychomycosis.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Mügge C, Haustein UF, Nenoff P. Causative agents of onychomycosis—A retrospective study. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2006;4:218–228. - PubMed
-
- Shemer A, Trau H, Davidovici B, Amichai B, Grunwald MH. Onychomycosis: Rationalization of topical treatment. Isr Med Assoc J 2008;10:415–416. - PubMed
-
- Tosti A, Hay R, Arenas‐Guzmán R. Patients at risk of onychomycosis—Risk factor identification and active prevention. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2005;19:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Ghannoum M, Hajjeh R, Scher R, et al. A large‐scale North American study of fungal isolates from nails: The frequency of onychomycosis, fungal distribution, and antifungal susceptibility patterns. J Am Acad Dermatol 2000;43:641–648. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

