Structural basis of recognition of farnesylated and methylated KRAS4b by PDEδ
- PMID: 27791178
- PMCID: PMC5098621
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1615316113
Structural basis of recognition of farnesylated and methylated KRAS4b by PDEδ
Abstract
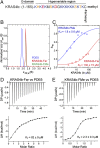
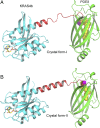
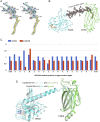
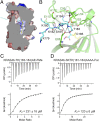
Farnesylation and carboxymethylation of KRAS4b (Kirsten rat sarcoma isoform 4b) are essential for its interaction with the plasma membrane where KRAS-mediated signaling events occur. Phosphodiesterase-δ (PDEδ) binds to KRAS4b and plays an important role in targeting it to cellular membranes. We solved structures of human farnesylated-methylated KRAS4b in complex with PDEδ in two different crystal forms. In these structures, the interaction is driven by the C-terminal amino acids together with the farnesylated and methylated C185 of KRAS4b that binds tightly in the central hydrophobic pocket present in PDEδ. In crystal form II, we see the full-length structure of farnesylated-methylated KRAS4b, including the hypervariable region. Crystal form I reveals structural details of farnesylated-methylated KRAS4b binding to PDEδ, and crystal form II suggests the potential binding mode of geranylgeranylated-methylated KRAS4b to PDEδ. We identified a 5-aa-long sequence motif (Lys-Ser-Lys-Thr-Lys) in KRAS4b that may enable PDEδ to bind both forms of prenylated KRAS4b. Structure and sequence analysis of various prenylated proteins that have been previously tested for binding to PDEδ provides a rationale for why some prenylated proteins, such as KRAS4a, RalA, RalB, and Rac1, do not bind to PDEδ. Comparison of all four available structures of PDEδ complexed with various prenylated proteins/peptides shows the presence of additional interactions due to a larger protein-protein interaction interface in KRAS4b-PDEδ complex. This interface might be exploited for designing an inhibitor with minimal off-target effects.
Keywords: KRAS4b; KRAS–PDEδ complex; phosphodiesterase-δ; prenylation; protein–protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



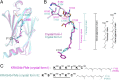



References
-
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. - PubMed
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: Conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991;349(6305):117–127. - PubMed
-
- Wittinghofer A, Pai EF. The structure of Ras protein: A model for a universal molecular switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991;16(10):382–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

