The Impact of Vitamin E and Other Fat-Soluble Vitamins on Alzheimer´s Disease
- PMID: 27792188
- PMCID: PMC5133786
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17111785
The Impact of Vitamin E and Other Fat-Soluble Vitamins on Alzheimer´s Disease
Abstract
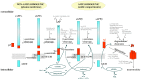
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia in the elderly population, currently affecting 46 million people worldwide. Histopathologically, the disease is characterized by the occurrence of extracellular amyloid plaques composed of aggregated amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles containing the microtubule-associated protein tau. Aβ peptides are derived from the sequential processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by enzymes called secretases, which are strongly influenced by the lipid environment. Several vitamins have been reported to be reduced in the plasma/serum of AD-affected individuals indicating they have an impact on AD pathogenesis. In this review we focus on vitamin E and the other lipophilic vitamins A, D, and K, and summarize the current knowledge about their status in AD patients, their impact on cognitive functions and AD risk, as well as their influence on the molecular mechanisms of AD. The vitamins might affect the generation and clearance of Aβ both by direct effects and indirectly by altering the cellular lipid homeostasis. Additionally, vitamins A, D, E, and K are reported to influence further mechanisms discussed to be involved in AD pathogenesis, e.g., Aβ-aggregation, Aβ-induced neurotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammatory processes, as summarized in this article.
Keywords: Alzheimer´s disease; lipids; tocopherol; tocotrienol; vitamin A; vitamin D; vitamin E; vitamin K.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
Role of Vitamin E in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 23;18(12):2504. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122504. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29168797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinations of Vitamin A and Vitamin E Metabolites Confer Resilience against Amyloid-β Aggregation.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Feb 15;14(4):657-666. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00523. Epub 2023 Feb 2. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36728544 Free PMC article.
-
Role of amyloid beta in lipid homeostasis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1801(8):966-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 May 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20452461 Review.
-
Fat-soluble vitamins.Annu Rev Biochem. 1958;27(3):371-402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.27.070158.002103. Annu Rev Biochem. 1958. PMID: 13571938 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Amylin and Secretases in the Pathology and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 17;12(7):996. doi: 10.3390/biom12070996. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K Properties in Stroke and Alzheimer's Disease: A Janus Bifrons in Protection and Prevention.Molecules. 2025 Feb 24;30(5):1027. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051027. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The detection of age-, gender-, and region-specific changes in mouse brain tocopherol levels via the application of different validated HPLC methods.Neurochem Res. 2018 Nov;43(11):2081-2091. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2630-8. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 30194607
-
Protection of cholinergic and antioxidant system contributes to the effect of Vitamin D3 ameliorating memory dysfunction in sporadic dementia of Alzheimer's type.Redox Rep. 2019 Dec;24(1):34-40. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2019.1617514. Redox Rep. 2019. PMID: 31100998 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Vitamin K2 Protection against Amyloid-β-Induced Cytotoxicity.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 13;11(3):423. doi: 10.3390/biom11030423. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33805625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Plassman B.L., Langa K.M., Fisher G.G., Heeringa S.G., Weir D.R., Ofstedal M.B., Burke J.R., Hurd M.D., Potter G.G., Rodgers W.L., et al. Prevalence of dementia in the united states: The aging, demographics, and memory study. Neuroepidemiology. 2007;29:125–132. doi: 10.1159/000109998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prince M., Wimo A., Guerchet M., Ali G.-C., Wu Y.T., Prina M., Alzheimers Disease International . World Alzheimer Report. Alzheimers Disease International; London, UK: 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

