FoxO1: a novel insight into its molecular mechanisms in the regulation of skeletal muscle differentiation and fiber type specification
- PMID: 27793012
- PMCID: PMC5354690
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12891
FoxO1: a novel insight into its molecular mechanisms in the regulation of skeletal muscle differentiation and fiber type specification
Abstract
FoxO1, a member of the forkhead transcription factor forkhead box protein O (FoxO) family, is predominantly expressed in most muscle types. FoxO1 is a key regulator of muscle growth, metabolism, cell proliferation and differentiation. In the past two decades, many researches have indicated that FoxO1 is a negative regulator of skeletal muscle differentiation while contrasting opinions consider that FoxO1 is crucial for myoblast fusion. FoxO1 is expressed much higher in fast twitch fiber enriched muscles than in slow muscles and is also closely related to muscle fiber type specification. In this review, we summarize the molecular mechanisms of FoxO1 in the regulation of skeletal muscle differentiation and fiber type specification.
Keywords: FoxO1; differentiation; fiber type specification; molecular mechanisms; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
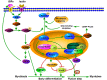

References
-
- de Lange P., Moreno M., Silvestri E., Lombardi A., Goglia F., Lanni A. Fuel economy in food-deprived skeletal muscle: signaling pathways and regulatory mechanisms. FASEB J. 2007;21:3431–3441. - PubMed
-
- Eijkelenboom A., Burgering B.M. FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nature reviews. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14:83–97. - PubMed
-
- Buckingham M. Skeletal muscle formation in vertebrates. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:440–448. - PubMed
-
- Pipes G.T., Creemers E.E., Olson E.N. The myocardin family of transcriptional coactivators: versatile regulators of cell growth, migration, and myogenesis. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1545–1556. - PubMed
-
- Potthoff M.J., Olson E.N. MEF2: a central regulator of diverse developmental programs. Development. 2007;134:4131–4140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

