Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal inflammatory response and apoptosis likely plays a key role in the development of diabetic encephalopathy
- PMID: 27793043
- PMCID: PMC5346653
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12925
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal inflammatory response and apoptosis likely plays a key role in the development of diabetic encephalopathy
Abstract
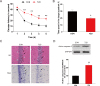
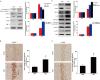
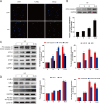
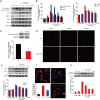
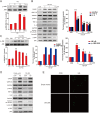
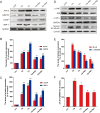
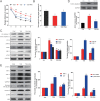
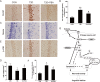
We assumed that diabetic encephalopathy (DEP) may be induced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mediated inflammation and apoptosis in central nervous system. To test this notion, here we investigated the neuronal ER stress and associated inflammation and apoptosis in a type 2 diabetes model induced with high-fat diet/streptozotocin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Elevated expressions of ER stress markers, including glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), activating transcription factor-6 (ATF-6), X-box binding protein-1 (XBP-1), and C/EBP homologous protein, and phosphor-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) were evident in the hippocampus CA1 of diabetic rats. These changes were also accompanied with the activation of NF-κB and the increased levels of inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6). Mechanistic study with in vitro cultured hippocampus neurons exposed to high glucose (HG), which induced a diabetes-like effects, shown by increased ER stress, JNK and NF-κB activation, and inflammatory response. Inhibition of ER stress by 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA) or blockade of JNK activity by specific inhibitor or transfection of DN-JNK attenuated HG-induced inflammation and associated apoptosis. To validate the in vitro finding, in vivo application of 4-PBA resulted in a significant reduction of diabetes-induced neuronal ER stress, inflammation and cell death, leading to the prevention of DEP. These results suggest that diabetes-induced neuronal ER stress plays the critical role for diabetes-induced neuronal inflammation and cell death, leading to the development of DEP.
Keywords: ER stress; apoptosis; diabetes; inflammation; p-JNK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict interest to disclosure
Figures
Similar articles
-
Terpene glycoside component from Moutan Cortex ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-related inflammatory responses.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 4;193:433-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.043. Epub 2016 Sep 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27664441
-
Selective, potent blockade of the IRE1 and ATF6 pathways by 4-phenylbutyric acid analogues.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;170(4):822-34. doi: 10.1111/bph.12306. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23869584 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress/autophagy pathway is involved in diabetes-induced neuronal apoptosis and cognitive decline in mice.Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Jan 11;132(1):111-125. doi: 10.1042/CS20171432. Print 2018 Jan 16. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29212786
-
Signaling pathways involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal apoptosis.Int J Neurosci. 2013 Mar;123(3):155-62. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2012.746974. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Int J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23134425 Review.
-
Inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity and diabetes.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Dec;32 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):S52-4. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.238. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 19136991 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine ameliorates rats model of combined Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus via the suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress.3 Biotech. 2020 Aug;10(8):359. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-02354-7. Epub 2020 Jul 29. 3 Biotech. 2020. PMID: 32832321 Free PMC article.
-
The IRE1/JNK signaling pathway regulates inflammation cytokines and production of glomerular extracellular matrix in the acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease transition.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Aug;49(8):7709-7718. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07588-7. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35696049
-
Secondary Mechanisms of Neurotrauma: A Closer Look at the Evidence.Diseases. 2022 May 23;10(2):30. doi: 10.3390/diseases10020030. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 35645251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ER stress and subsequent activated calpain play a pivotal role in skeletal muscle wasting after severe burn injury.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 13;12(10):e0186128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186128. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29028830 Free PMC article.
-
Control of macrophage autophagy by miR-384-5p in the development of diabetic encephalopathy.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Feb 15;10(2):511-518. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29511445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sima AA, Li ZG. The effect of C-peptide on cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal apoptosis in type 1 diabetic rats. Diabetes. 2005;54:1497–1505. - PubMed
-
- Mijnhout GS, Scheltens P, Diamant M, Biessels GJ, Wessels AM, Simsek S, Snoek FJ, Heine RJ. Diabetic encephalopathy: A concept in need of a definition. Diabetologia. 2006;49:1447–1448. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

