Genome sequence of Phormia regina Meigen (Diptera: Calliphoridae): implications for medical, veterinary and forensic research
- PMID: 27793085
- PMCID: PMC5084420
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-3187-z
Genome sequence of Phormia regina Meigen (Diptera: Calliphoridae): implications for medical, veterinary and forensic research
Abstract
Background: Blow flies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) are important medical, veterinary and forensic insects encompassing 8 % of the species diversity observed in the calyptrate insects. Few genomic resources exist to understand the diversity and evolution of this group.
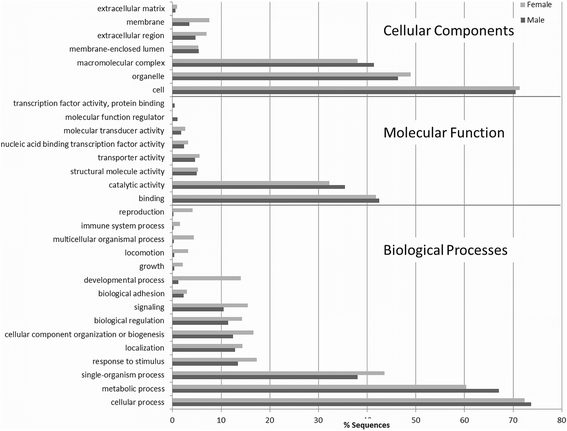
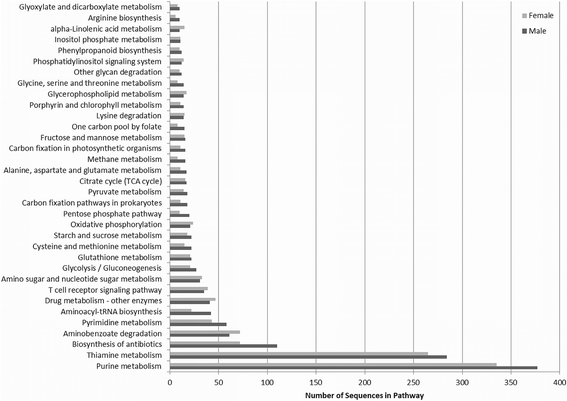
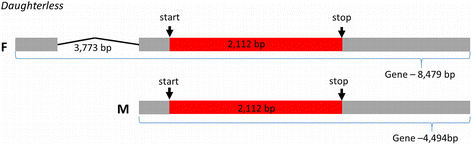
Results: We present the hybrid (short and long reads) draft assemblies of the male and female genomes of the common North American blow fly, Phormia regina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). The 550 and 534 Mb draft assemblies contained 8312 and 9490 predicted genes in the female and male genomes, respectively; including > 93 % conserved eukaryotic genes. Putative X and Y chromosomes (21 and 14 Mb, respectively) were assembled and annotated. The P. regina genomes appear to contain few mobile genetic elements, an almost complete absence of SINEs, and most of the repetitive landscape consists of simple repetitive sequences. Candidate gene approaches were undertaken to annotate insecticide resistance, sex-determining, chemoreceptors, and antimicrobial peptides.
Conclusions: This work yielded a robust, reliable reference calliphorid genome from a species located in the middle of a calliphorid phylogeny. By adding an additional blow fly genome, the ability to tease apart what might be true of general calliphorids vs. what is specific of two distinct lineages now exists. This resource will provide a strong foundation for future studies into the evolution, population structure, behavior, and physiology of all blow flies.
Keywords: Blow fly; Calliphoridae; Genome; Phormia regina; Sex determination; X chromosome; Y chromosome.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

