Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation
- PMID: 27793571
- PMCID: PMC5205568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2016.10.001
Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and Inflammation
Abstract
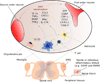
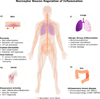
Nociceptor sensory neurons protect organisms from danger by eliciting pain and driving avoidance. Pain also accompanies many types of inflammation and injury. It is increasingly clear that active crosstalk occurs between nociceptor neurons and the immune system to regulate pain, host defense, and inflammatory diseases. Immune cells at peripheral nerve terminals and within the spinal cord release mediators that modulate mechanical and thermal sensitivity. In turn, nociceptor neurons release neuropeptides and neurotransmitters from nerve terminals that regulate vascular, innate, and adaptive immune cell responses. Therefore, the dialog between nociceptor neurons and the immune system is a fundamental aspect of inflammation, both acute and chronic. A better understanding of these interactions could produce approaches to treat chronic pain and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: inflammation; neuroimmunology; nociceptor; pain; sensory neuron.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Wood JN, et al. Voltage-gated sodium channels and pain pathways. J. Neurobiol. 2004;61:55–71. - PubMed
-
- Cunha TM, et al. Crucial role of neutrophils in the development of mechanical inflammatory hypernociception. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008;83:824–832. - PubMed
-
- Kiguchi N, et al. Epigenetic Augmentation of the Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 2/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 2 Axis through Histone H3 Acetylation in Injured Peripheral Nerves Elicits Neuropathic Pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012;340:577–587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

