Sporadic and Infectious Human Prion Diseases
- PMID: 27793965
- PMCID: PMC5204333
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a024364
Sporadic and Infectious Human Prion Diseases
Abstract
Human prion diseases are rare neurodegenerative diseases that have become the subject of public and scientific interest because of concerns about interspecies transmission and the unusual biological properties of the causal agents: prions. These diseases are unique in that they occur in sporadic, hereditary, and infectious forms that are characterized by an extended incubation period between exposure to infection and the development of clinical illness. Silent infection can be present in peripheral tissues during the incubation period, which poses a challenge to public health, especially because prions are relatively resistant to standard decontamination procedures. Despite intense research efforts, no effective treatment has been developed for human prion diseases, which remain uniformly fatal.
Copyright © 2017 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
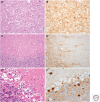

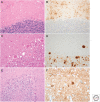
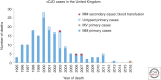
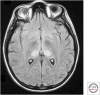
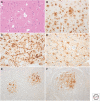
References
-
- Alcalde-Cabero E, Almazán-Isla J, Brandel JP, Breithaupt M, Catarino J, Collins S, Haybäck J, Höftberger R, Kahana E, Kovacs GG, et al. 2012. Health professionals and risk of sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, 1965 to 2010. Eurosurveillance 17: 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Barbot C, Castro L, Oliveira C, Carpenter C. 2010. Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: The first confirmed cases from Portugal shows early onset, long duration and unusual pathology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81: 112–115. - PubMed
-
- Binelli S, Agazzi P, Giaccone G, Will RG, Bugiani O, Franceschetti S, Tagliavini F. 2006. Periodic electroencephalogram complexes in a patient with variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Ann Neurol 59: 423–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
