Association of UGT2B7 and UGT1A4 Polymorphisms with Serum Concentration of Antiepileptic Drugs in Children
- PMID: 27795544
- PMCID: PMC5100833
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.897626
Association of UGT2B7 and UGT1A4 Polymorphisms with Serum Concentration of Antiepileptic Drugs in Children
Abstract
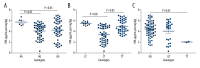
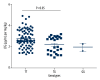
BACKGROUND This study aimed to analyze the relationship of UGT2B7 and UGT1A4 polymorphisms with metabolism of valproic acid (VPA) and lamotrigine (LTG) in epileptic children. MATERIAL AND METHODS We administered VPA (102) and LTG (102) to 204 children with epilepsy. Blood samples were collected before the morning dose. Serum concentration of LTG was measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Serum VPA concentration was tested by fluorescence polarization immunoassay. UGT2B7 A268G, C802T, and G211T polymorphisms, as well as UGT1A4 L48V polymorphism, were assayed by direct automated DNA sequencing after PCR. Evaluation of efficacy was conducted using the Engel method. RESULTS The adjusted serum concentration of VPA was 4.26 μg/mL per mg/kg and LTG was 1.56 μg/mL per mg/kg. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that VPA or LTG adjusted concentration showed a good linear relation with sex and age. UGT2B7 A268G and C802T polymorphisms were demonstrated to affect the serum concentration of VPA (F=3.147, P=0.047; F=22.754, P=0.000). UGT1A4 L48V polymorphism was not related with the serum concentration of LTG (F=5.328, P=0.006). In the efficacy analysis, we found that C802T polymorphism exerted strong effects on efficacy of VPA (χ²=9.265, P=0.010). L48V polymorphism also showed effects on efficacy of LTG (χ²=17.397, P=0.001). CONCLUSIONS UGT2B7, UGT1A4 polymorphisms play crucial roles in metabolism of VPA and LTG.
Figures
References
-
- Thurman DJ, Beghi E, Begley CE, et al. Standards for epidemiologic studies and surveillance of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2011;52(Suppl 7):2–26. - PubMed
-
- Kotsopoulos IA, van Merode T, Kessels FG, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of incidence studies of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures. Epilepsia. 2002;43(11):1402–9. - PubMed
-
- Tellez-Zenteno JF, Patten SB, Jetté N, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity in epilepsy: A population-based analysis. Epilepsia. 2007;48(12):2336–44. - PubMed
-
- Kobau R, Zahran H, Thurman DJ, et al. Epilepsy surveillance among adults – 19 States, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2005. Surveill Summ. 2008;57(6):1–20. - PubMed