Hemodialysis among pregnancy related acute kidney injury patients: A single center experience in North-Western Nigeria
- PMID: 27795627
- PMCID: PMC5015511
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-4065.171224
Hemodialysis among pregnancy related acute kidney injury patients: A single center experience in North-Western Nigeria
Abstract
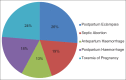
Pregnancy related acute kidney injury (PRAKI) patients that underwent hemodialysis (HD) between May 2007 and April 2015 were studied with specific reference to clinical features, laboratory values, duration of pregnancy at the diagnosis of acute kidney injury and outcome. It involved 38 patients aged between 15 and 30 years. The main clinical features were fever, edema and oliguria. The leading etiological factors included ante/postpartum hemorrhage, septic abortion, and toxemia of pregnancy. The majority of cases occurred during the third trimester. PRAKI is a dreaded complication of pregnancy with high morbidity and mortality. HD improved patient survival in our study.
Keywords: Hemodialysis; pregnancy; pregnancy related acute kidney injury.
Figures
References
-
- Chijioke A, Makusidi AM. Severe acute kidney injury in adult in Nigerians. BOMJ. 2011;29:311–4.
-
- Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R. Acute renal failure. Lancet. 2005;365:417–30. - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M, Manns B, Feller-Kopman D. Acute renal failure in the intensive care unit: A systematic review of the impact of dialytic modality on mortality and renal recovery. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;40:875–85. - PubMed
-
- Rani PU, Narayen G. Changing trends in pregnancy related acute renal failure. J Obstet Gynecol India. 2002;8:36–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous