INTEGRATE-neo: a pipeline for personalized gene fusion neoantigen discovery
- PMID: 27797777
- PMCID: PMC5408800
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw674
INTEGRATE-neo: a pipeline for personalized gene fusion neoantigen discovery
Abstract
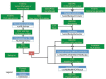
Motivation: While high-throughput sequencing (HTS) has been used successfully to discover tumor-specific mutant peptides (neoantigens) from somatic missense mutations, the field currently lacks a method for identifying which gene fusions may generate neoantigens.
Results: We demonstrate the application of our gene fusion neoantigen discovery pipeline, called INTEGRATE-Neo, by identifying gene fusions in prostate cancers that may produce neoantigens.
Availability and implementation: INTEGRATE-Neo is implemented in C ++ and Python. Full source code and installation instructions are freely available from https://github.com/ChrisMaherLab/INTEGRATE-Neo .
Contact: christophermaher@wustl.edu.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases