Expression Variations of miRNAs and mRNAs in Rice (Oryza sativa)
- PMID: 27797952
- PMCID: PMC5203789
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evw252
Expression Variations of miRNAs and mRNAs in Rice (Oryza sativa)
Abstract
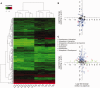
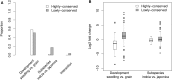
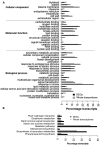
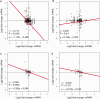
Differences in expression levels are an important source of phenotypic variation within and between populations. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key players in post-transcriptional gene regulation that are important for plant development and stress responses. We surveyed expression variation of miRNAs and mRNAs of six accessions from two rice subspecies Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica and Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica using deep sequencing. While more than half (53.7%) of the mature miRNAs exhibit differential expression between grains and seedlings of rice, only 11.0% show expression differences between subspecies, with an additional 2.2% differentiated for the development-by-subspecies interaction. Expression variation is greater for lowly conserved miRNAs than highly conserved miRNAs, whereas the latter show stronger negative correlation with their targets in expression changes between subspecies. Using a permutation test, we identified 51 miRNA-mRNA pairs that correlate negatively or positively in expression level among cultivated rice. Genes involved in various metabolic processes and stress responses are enriched in the differentially expressed genes between rice indica and japonica subspecies. Our results indicate that stabilizing selection is the major force governing miRNA expression in cultivated rice, albeit positive selection may be responsible for much of the between-subspecies expression divergence.
Keywords: expression variation; mRNA; microRNA; rice.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures
References
-
- Alon U. 2007. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet. 8(6):450–461. - PubMed
-
- Axtell MJ. 2013. Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 64:137–159. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

