Modelling C9orf72 dipeptide repeat proteins of a physiologically relevant size
- PMID: 27798094
- PMCID: PMC5886041
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddw327
Modelling C9orf72 dipeptide repeat proteins of a physiologically relevant size
Abstract
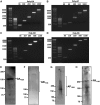
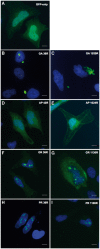
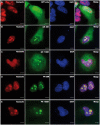
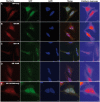
C9orf72 expansions are the most common genetic cause of FTLD and MND identified to date. Although being intronic, the expansion is translated into five different dipeptide repeat proteins (DPRs) that accumulate within patients' neurons. Attempts have been made to model DPRs in cell and animals. However, the majority of these use DPRs repeat numbers much shorter than those observed in patients. To address this we have generated a selection of DPR expression constructs with repeat numbers in excess of 1000 repeats, matching what is seen in patients. Small and larger DPRs produce inclusions with similar morphology but different cellular effects. We demonstrate a length dependent effect using electrophysiology with a phenotype only occurring with the longest DPRs. These data highlight the importance of using physiologically relevant repeat numbers when modelling DPRs.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



References
-
- Majounie E., Renton A.E., Mok K., Dopper E.G., Waite A., Rollinson S., Chio A., Restagno G., Nicolaou N., Simon-Sanchez J., et al. (2012) Frequency of the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol., 11, 323–330. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

