Considering the Optimal Timing of Breast Reconstruction With Abdominal Flaps With Adjuvant Irradiation in 370 Consecutive Pedicled Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap and Free Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Performed in a Chinese Oncology Center: Is There a Significant Difference Between Immediate and Delayed?
- PMID: 27798424
- PMCID: PMC5434969
- DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000927
Considering the Optimal Timing of Breast Reconstruction With Abdominal Flaps With Adjuvant Irradiation in 370 Consecutive Pedicled Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap and Free Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Performed in a Chinese Oncology Center: Is There a Significant Difference Between Immediate and Delayed?
Abstract
Purpose: There is an ongoing debate on the optimal sequence of radiation and breast reconstruction. The purpose of this article was to (a) assess the impact of radiation on autologous breast reconstruction and (b) analyze the best timing for autologous breast reconstruction in the setting of radiation in a Chinese population.
Methods: A retrospective review of patients undergoing breast reconstruction with autologous lower abdominal flaps between 2001 and 2014 in the Tianjin Medical University and Cancer Hospital was performed. Patients were grouped by their irradiation status (irradiated vs nonirradiated). The irradiated group was further stratified into 2 groups by the timing of irradiation (immediate breast reconstruction followed by radiation vs prior radiation and delayed breast reconstruction). The primary outcomes were early and late breast complications, secondary and revision surgeries to the reconstructed breast, whereas the secondary outcomes were aesthetic and psychological evaluations of the patients. Logistic regression was used to assess the potential association between irradiation, patient and treatment variables, and surgical outcomes.
Results: Three hundred sixty patients with 370 reconstructed breasts were included in the study. Two hundred seventy-eight cases were nonirradiated, of which 158 were immediate and 120 were delayed. Ninety-two cases were irradiated, of which 61 were immediate, and 31 were delayed. Three hundred thirty-two cases underwent pedicled transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap, 38 had deep inferior epigastric perforator flap. The irradiated group had a significant increase in secondary surgery due to fat necrosis (P < 0.001) and in late complications (P = 0.011). A significant increase in flap contracture (P = 0.043) and an increasing trend in the severity of fat necrosis were observed when radiation was performed after breast reconstruction. However, radiation and its timing did not have an adverse impact on patients' aesthetic and psychological evaluations by the Breast-Q survey.
Conclusions: Radiation administered to the reconstructed breast mound increased the rate of late complications and the need for secondary surgery with increased abdominal flap shrinkage and contracture and the severity of flap fat necrosis. Irradiation on the reconstructed breast did not lead to worse aesthetic outcomes due to the generally different expectation in the Chinese female patients in that they were more focused on the breast shape when clothed. Immediate breast reconstruction followed by irradiated was a generally successful treatment sequence in the Chinese module.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest and sources of funding: none declared.
Figures

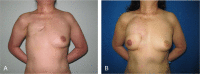
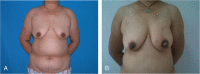
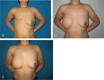
References
-
- Ragaz J, Jackson SM, Le N, et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy in node-positive premenopausal women with breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:956–962. - PubMed
-
- Overgaard M, Hansen PS, Overgaard J, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group 82b Trial. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:949–955. - PubMed
-
- Classen J, Nitzsche S, Wallwiener D, et al. Fibrotic changes after postmastectomy radiotherapy and reconstructive surgery in breast cancer. A retrospective analysis in 109 patients. Strahlenther Onkol. 2010;186:630–636. - PubMed
-
- Schaverien MV, Macmillan RD, McCulley SJ. Is immediate autologous breast reconstruction with postoperative radiotherapy good practice? A systematic review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66:1637–1651. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

