S-2-hydroxyglutarate regulates CD8+ T-lymphocyte fate
- PMID: 27798602
- PMCID: PMC5149074
- DOI: 10.1038/nature20165
S-2-hydroxyglutarate regulates CD8+ T-lymphocyte fate
Abstract
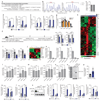
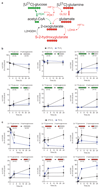
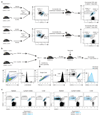
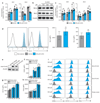
R-2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates to millimolar levels in cancer cells with gain-of-function isocitrate dehydrogenase 1/2 mutations. These levels of R-2-hydroxyglutarate affect 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Both metabolite enantiomers, R- and S-2-hydroxyglutarate, are detectible in healthy individuals, yet their physiological function remains elusive. Here we show that 2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates in mouse CD8+ T cells in response to T-cell receptor triggering, and accumulates to millimolar levels in physiological oxygen conditions through a hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α)-dependent mechanism. S-2-hydroxyglutarate predominates over R-2-hydroxyglutarate in activated T cells, and we demonstrate alterations in markers of CD8+ T-cell differentiation in response to this metabolite. Modulation of histone and DNA demethylation, as well as HIF-1α stability, mediate these effects. S-2-hydroxyglutarate treatment greatly enhances the in vivo proliferation, persistence and anti-tumour capacity of adoptively transferred CD8+ T cells. Thus, S-2-hydroxyglutarate acts as an immunometabolite that links environmental context, through a metabolic-epigenetic axis, to immune fate and function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




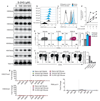

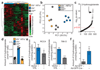

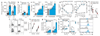

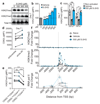
Comment in
-
S-2HG is an immunometabolite that shapes the T-cell response.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Feb;24(2):195-196. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.149. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28009351 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

