Prediction of Hospitalization due to Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly Community-Dwelling Patients (The PADR-EC Score)
- PMID: 27798708
- PMCID: PMC5087856
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165757
Prediction of Hospitalization due to Adverse Drug Reactions in Elderly Community-Dwelling Patients (The PADR-EC Score)
Abstract
Background: Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are the major cause of medication-related hospital admissions in older patients living in the community. This study aimed to develop and validate a score to predict ADR-related hospitalization in people aged ≥65 years.
Methods: ADR-related hospitalization and its risk factors were determined using a prospective, cross-sectional study in patients aged ≥65 years admitted to two hospitals. A predictive model was developed in the derivation cohort (n = 768) and the model was applied in the validation cohort (n = 240). ADR-related hospital admission was determined through expert consensus from comprehensive reviews of medical records and patient interviews. The causality and preventability of the ADR were assessed based on the Naranjo algorithm and modified Schumock and Thornton criteria, respectively.
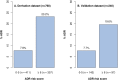
Results: In the derivation sample (mean [±SD] age, 80.1±7.7 years), 115 (15%) patients were admitted due to a definite or probable ADR; 92.2% of these admissions were deemed preventable. The number of antihypertensives was the strongest predictor of an ADR followed by presence of dementia, renal failure, drug changes in the preceding 3 months and use of anticholinergic medications; these variables were used to derive the ADR prediction score. The predictive ability of the score, assessed from calculation of the area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve, was 0.70 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.65-0.75). In the validation sample (mean [±SD] age, 79.6±7.6 years), 30 (12.5%) patients' admissions were related to definite or probable ADRs; 80% of these admissions were deemed preventable. The area under the ROC curve in this sample was 0.67 (95% CI 0.56-0.78).
Conclusions: This study proposes a practical and simple tool to identify elderly patients who are at an increased risk of preventable ADR-related hospital admission. Further refinement and testing of this tool is necessary to implement the score in clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Franceschi M, Scarcelli C, Niro V, Seripa D, Pazienza AM, Pepe G, et al. Prevalence, clinical features and avoidability of adverse drug reactions as cause of admission to a geriatric unit: a prospective study of 1756 patients. Drug Saf. 2008;31(6):545–56. - PubMed
-
- Gurwitz JH, Field TS, Harrold LR, Rothschild J, Debellis K, Seger AC, et al. Incidence and preventability of adverse drug events among older persons in the ambulatory setting. JAMA. 2003;289(9):1107–16. - PubMed
-
- Hanlon JT, Schmader KE, Koronkowski MJ, Weinberger M, Landsman PB, Samsa GP, et al. Adverse drug events in high risk older outpatients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(8):945–8. - PubMed
-
- Mannesse CK, Derkx FH, de Ridder MA, Man in 't Veld AJ, van der Cammen TJ. Contribution of adverse drug reactions to hospital admission of older patients. Age Ageing. 2000;29(1):35–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

