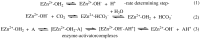A class of carbonic anhydrase I - selective activators
- PMID: 27798977
- PMCID: PMC6010081
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2016.1232254
A class of carbonic anhydrase I - selective activators
Abstract
A series of ureido and bis-ureido derivatives were prepared by reacting histamine with alkyl/aryl-isocyanates or di-isocyanates. The obtained derivatives were assayed as activators of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1), due to the fact that histamine itself has this biological activity. Although inhibition of CAs has pharmacological applications in the field of antiglaucoma, anticonvulsant, anticancer, and anti-infective agents, activation of these enzymes is not yet properly exploited pharmacologically for cognitive enhancement or Alzheimer's disease treatment, conditions in which a diminished CA activity was reported. The ureido/bis-ureido histamine derivatives investigated here showed activating effects only against the cytosolic human (h) isoform hCA I, having no effect on the widespread, physiologically dominant isoform hCA II. This is the first report in which CA I-selective activators were identified. Such compounds may constitute interesting tools for better understanding the physiological/pharmacological effects connected to activation of this widespread CA isoform, whose physiological function is not fully understood.
Keywords: Anchoring to zinc-coordinated water; carbonic anhydrase; inhibition mechanism; inhibitors; occlusion of the active site entrance; out of the active site binding.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carbonic anhydrases activation with 3-amino-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-carboxamides: Discovery of subnanomolar isoform II activators.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Mar 1;25(5):1681-1686. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.031. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28161251
-
Carbonic anhydrase activators: high affinity isozymes I, II, and IV activators, incorporating a beta-alanyl-histidine scaffold.J Med Chem. 2002 Jan 17;45(2):284-91. doi: 10.1021/jm010958k. J Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11784133
-
Carbonic anhydrase activators. The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors fluoxetine, sertraline and citalopram are strong activators of isozymes I and II.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Aug 18;13(16):2765-8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(03)00507-9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003. PMID: 12873510
-
Designing of novel carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and activators.Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2004 Jan;2(1):49-68. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2004. PMID: 15328829 Review.
-
How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist?J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016;31(3):345-60. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2015.1122001. Epub 2015 Nov 30. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26619898 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of amino acids and amines on the activity of the recombinant ι-carbonic anhydrase from the Gram-negative bacterium Burkholderia territorii.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):1000-1006. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1919891. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33980103 Free PMC article.
-
Five- and Six-Membered Nitrogen-Containing Compounds as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase Activators.Molecules. 2017 Dec 9;22(12):2178. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122178. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29232847 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of piperazines as human carbonic anhydrase I, II, IV and VII activators.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018 Dec;33(1):303-308. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1417277. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29280407 Free PMC article.
-
Activation Profile Analysis of CruCA4, an α-Carbonic Anhydrase Involved in Skeleton Formation of the Mediterranean Red Coral, Corallium rubrum.Molecules. 2017 Dec 28;23(1):66. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010066. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29283417 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic Anhydrase Activators for Neurodegeneration: An Overview.Molecules. 2022 Apr 14;27(8):2544. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082544. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Supuran CT.Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008;7:168–81. - PubMed
-
- Neri D, Supuran CT. Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011;10:767–77. - PubMed
-
- Capasso C, Supuran CT.. An overview of the alpha-, beta-and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from bacteria: can bacterial carbonic anhydrases shed new light on evolution of bacteria? J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2015;30:325–32. - PubMed
-
- Supuran CT, Capasso C. The η-class carbonic anhydrases as drug targets for antimalarial agents. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2015;19:551–63. - PubMed
-
- Supuran CT.Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2012;27:759–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous