PTPN22 contributes to exhaustion of T lymphocytes during chronic viral infection
- PMID: 27799548
- PMCID: PMC5135306
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1603738113
PTPN22 contributes to exhaustion of T lymphocytes during chronic viral infection
Abstract
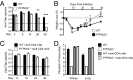
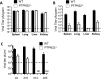
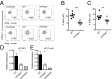
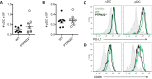
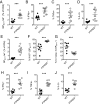
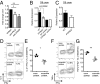
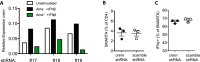
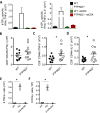
The protein encoded by the autoimmune-associated protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 22 gene, PTPN22, has wide-ranging effects in immune cells including suppression of T-cell receptor signaling and promoting efficient production of type I interferons (IFN-I) by myeloid cells. Here we show that mice deficient in PTPN22 resist chronic viral infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus clone 13 (LCMV cl13). The numbers and function of viral-specific CD4 T lymphocytes is greatly enhanced, whereas expression of the IFNβ-induced IL-2 repressor, cAMP-responsive element modulator (CREM) is reduced. Reduction of CREM expression in wild-type CD4 T lymphocytes prevents the loss of IL-2 production by CD4 T lymphocytes during infection with LCMV cl13. These findings implicate the IFNβ/CREM/IL-2 axis in regulating T-lymphocyte function during chronic viral infection.
Keywords: CREM; LCMV; PTPN22; T-cell exhaustion; chronic infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wherry EJ. T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(6):492–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

