LRRK2 inhibitors and their potential in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: current perspectives
- PMID: 27799832
- PMCID: PMC5076802
- DOI: 10.2147/CPAA.S102191
LRRK2 inhibitors and their potential in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: current perspectives
Abstract
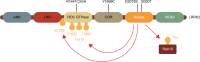
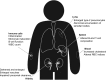
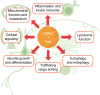
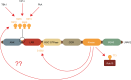
Major advances in understanding how genetics underlies Parkinson's disease (PD) have provided new opportunities for understanding disease pathogenesis and potential new targets for therapeutic intervention. One such target is leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), an enigmatic enzyme implicated in both familial and idiopathic PD risk. Both academia and industry have promoted the development of potent and selective inhibitors of LRRK2, and these are currently being employed to assess the safety and efficacy of such compounds in preclinical models of PD. This review examines the evidence that LRRK2 kinase activity contributes to the pathogenesis of PD and outlines recent progress on inhibitor development and early results from preclinical safety and efficacy testing. This review also looks at some of the challenges remaining for translation of LRRK2 inhibitors to the clinic, if indeed this is ultimately warranted. As a disease with no current cure that is increasing in prevalence in line with an aging population, there is much need for developing new treatments for PD, and targeting LRRK2 is currently a promising option.
Keywords: Rab; autophagy; inflammation; inhibitor; lysosome; synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Xilouri M, Brekk OR, Stefanis L. Autophagy and alpha-synuclein: relevance to Parkinson’s disease and related synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2016;31(2):178–192. - PubMed
-
- Bose A, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2016 Aug 21; Epub. - PubMed
-
- Ryan BJ, Hoek S, Fon EA, Wade-Martins R. Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy in Parkinson’s: from familial to sporadic disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015;40(4):200–210. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

