Prevalence of Virulence-Related Determinants in Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 27800129
- PMCID: PMC5078722
- DOI: 10.5812/jjm.30593
Prevalence of Virulence-Related Determinants in Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus epidermidis, a member of the human flora, is recognized as an opportunistic pathogen and cause of nosocomial infections. Staphylococcus epidermidis surface components are able to establish bacteria on the host surface, and cause infection.
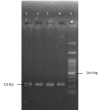
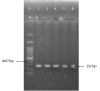
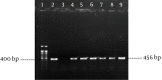
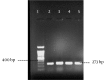
Objectives: The frequency of icaA, IS256, aap, fbe and bhp in clinical isolates of S. epidermidis were investigated in this study.
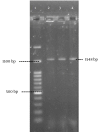
Materials and methods: Fifty-nine S. epidermidis isolates were collected from blood (50), wound (1), urine (4) and tracheal (4) samples (Tehran, Iran). Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates were identified with conventional bacteriological tests. Virulence-associated genes were detected by specific polymerase chain reactions (PCRs).
Results: Of the 59 S. epidermidis, fbe was found in 89.8%, while aap and bhp were observed in 64.4% and 15.3% of the samples, respectively. Coexistence of aap and fbe was found in 32 isolates, while coexistence of bhp and fbe was observed in five isolates. Two isolates were negative for the investigated genes.
Conclusions: Prevalence of fbe and aap was significantly different from similar studies, yet frequency of bhp was in accordance with other studies. Prevalence of icaA and IS256 was not significantly different from some studies while a significant difference was observed when results were compared with some other studies.
Keywords: Staphylococcal Infections; Staphylococcus epidermidis; Virulence Factors.
Figures
References
-
- Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284(5418):1318–22. - PubMed
-
- Davis SL, Gurusiddappa S, McCrea KW, Perkins S, Hook M. SdrG, a fibrinogen-binding bacterial adhesin of the microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules subfamily from Staphylococcus epidermidis, targets the thrombin cleavage site in the Bbeta chain. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(30):27799–805. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103873200. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
