Effect of Culture Condition Variables on Human Endostatin Gene Expression in Escherichia coli Using Response Surface Methodology
- PMID: 27800134
- PMCID: PMC5080621
- DOI: 10.5812/jjm.34091
Effect of Culture Condition Variables on Human Endostatin Gene Expression in Escherichia coli Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
Background: Recombinant human endostatin (rhES) is an angiogenesis inhibitor used as a specific drug for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. As mRNA concentration affects the recombinant protein expression level, any factor affecting mRNA concentration can alter the protein expression level. Response surface methodology (RSM) based on the Box-Behnken design (BBD) is a statistical tool for experimental design and for optimizing biotechnological processes.
Objectives: This investigation aimed to predict and develop the optimal culture conditions for mRNA expression of the synthetic human endostatin (hES) gene in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3).
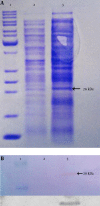
Materials and methods: The hES gene was amplified, cloned, and expressed in the E. coli expression system. Three factors, including isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) concentration, post-induction time, and cell density before induction, were selected as important factors. The mRNA expression level was determined using real-time PCR. The expression levels of hES mRNA under the different growth conditions were analyzed. SDS-PAGE and western blot analyses were carried out for further confirmation of interest-gene expression.
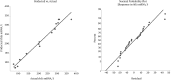
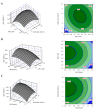
Results: A maximum rhES mRNA level of 376.16% was obtained under the following conditions: 0.6 mM IPTG, 7 hours post-induction time, and 0.9 cell density before induction. The level of rhES mRNA was significantly correlated with post-induction time, IPTG concentration, and cell density before induction (P < 0.05). The expression of the hES gene was confirmed by western blot.
Conclusions: The obtained results indicate that RSM is an effective method for the optimization of culture conditions for hES gene expression in E. coli.
Keywords: Angiogenesis Inhibitors; Endostatin; Escherichia coli; Gene Expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression and Secretion of Endostar Protein by Escherichia Coli: Optimization of Culture Conditions Using the Response Surface Methodology.Mol Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;58(10):634-647. doi: 10.1007/s12033-016-9963-9. Mol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27377615
-
Cloning and Expression of Recombinant Human Endostatin in Periplasm of Escherichia coli Expression System.Adv Pharm Bull. 2016 Jun;6(2):187-94. doi: 10.15171/apb.2016.026. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016. PMID: 27478780 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of culture conditions for Mpt64 synthetic gene expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) using surface response methodology.Heliyon. 2019 Nov 28;5(11):e02741. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02741. eCollection 2019 Nov. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31844694 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Fermentation Conditions for Recombinant Human Interferon Beta Production by Escherichia coli Using the Response Surface Methodology.Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015 Apr 18;8(4):e16236. doi: 10.5812/jjm.8(4)2015.16236. eCollection 2015 Apr. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26034535 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing recombinant production of L-asparaginase 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae using response surface methodology.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024 Dec;69(6):1205-1219. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01163-2. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024. PMID: 38581537
Cited by
-
Implementation of a Design of Experiments to Improve Periplasmic Yield of Functional ScFv Antibodies in a Phage Display Platform.Adv Pharm Bull. 2022 May;12(3):583-592. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.061. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35935041 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Secretion of Endostar Protein by Escherichia Coli: Optimization of Culture Conditions Using the Response Surface Methodology.Mol Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;58(10):634-647. doi: 10.1007/s12033-016-9963-9. Mol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27377615
-
The Challenges of Recombinant Endostatin in Clinical Application: Focus on the Different Expression Systems and Molecular Bioengineering.Adv Pharm Bull. 2017 Apr;7(1):21-34. doi: 10.15171/apb.2017.004. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28507934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient biomass saccharification using a novel cellobiohydrolase from Clostridium clariflavum for utilization in biofuel industry.RSC Adv. 2021 Mar 1;11(16):9246-9261. doi: 10.1039/d1ra00545f. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Du C, Yi X, Zhang Y. Expression and purification of soluble recombinant Human Endostatin in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2010;15(2):229–35. doi: 10.1007/s12257-009-0100-5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
