Tunable Helicity, Stability and DNA-Binding Properties of Short Peptides with Hybrid Metal Coordination Motifs
- PMID: 27800151
- PMCID: PMC5085262
- DOI: 10.1039/C6SC00826G
Tunable Helicity, Stability and DNA-Binding Properties of Short Peptides with Hybrid Metal Coordination Motifs
Abstract
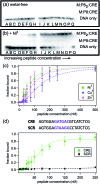
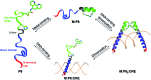
Given the prevalent role of α-helical motifs on protein surfaces in mediating protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions, there have been significant efforts to develop strategies to induce α-helicity in short, unstructured peptides to interrogate such interactions. Toward this goal, we have recently introduced hybrid metal coordination motifs (HCMs). HCMs combine a natural metal-binding amino acid side chain with a synthetic chelating group that are appropriately positioned in a peptide sequence to stabilize an α-helical conformation upon metal coordination. Here, we present a series of short peptides modified with HCMs consisting of a His and a phenanthroline group at i and i+7 positions that can induce α-helicity in a metal-tunable fashion as well as direct the formation of discrete dimeric architectures for recognition of biological targets. We show that the induction of α-helicity can be further modulated by secondary sphere interactions between amino acids at the i+4 position and the HCM. A frequently cited drawback of the use of peptides as therapeutics is their propensity to be quickly digested by proteases; here, we observe an enhancement of up to ∼100-fold in the half-lifes of the metal-bound HCM-peptides in the presence of trypsin. Finally, we show that an HCM-bearing peptide sequence, which contains the DNA-recognition domain of a bZIP protein but is devoid of the obligate dimerization domain, can dimerize with the proper geometry and in an α-helical conformation to bind a cognate DNA sequence with high affinities (Kd≥ 65 nM), again in a metal-tunable manner.
Figures
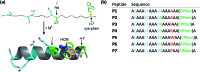




References
-
- Burkhard P., Stetefeld J., Strelkov S. V. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:82–88. - PubMed
-
- Lupas A. N. and Gruber M., in Advances in Protein Chemistry, Academic Press, 2005, vol. 70, pp. 37–38. - PubMed
-
- Youle R. J., Strasser A. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Kussie P. H., Gorina S., Marechal V., Elenbaas B., Moreau J., Levine A. J., Pavletich N. P. Science. 1996;274:948–953. - PubMed
-
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Trends Genet. 1990;6:36–40. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

