Effects of Suilysin on Streptococcus suis-Induced Platelet Aggregation
- PMID: 27800304
- PMCID: PMC5065993
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00128
Effects of Suilysin on Streptococcus suis-Induced Platelet Aggregation
Abstract
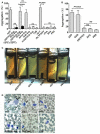
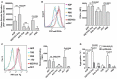
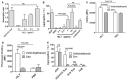
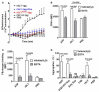
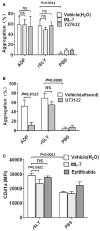
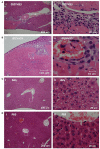
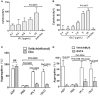
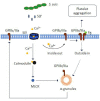
Blood platelets play important roles during pathological thrombocytopenia in streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS). Streptococcus suis (S. suis) an emerging human pathogen, can cause STSS similarly to S. pyogenes. However, S. suis interactions with platelets are poorly understood. Here, we found that suilysin (SLY), different from other bacterial cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs), was the sole stimulus that induced platelet aggregation. Furthermore, the inside-out activation of GPIIb/IIIa of platelets mediated SLY-induced platelet aggregation. This process was triggered by Ca2+ influx that depend on the pore forming on platelets by SLY. Additionally, although SLY induced α-granule release occurred via the MLCK-dependent pathway, PLC-β-IP3/DAG-MLCK and Rho-ROCK-MLCK signaling were not involved in SLY-induced platelet aggregation. Interestingly, the pore dependent Ca2+ influx was also found to participate in the induction of platelet aggregation with pneumolysin (PLY) and streptolysin O (SLO), two other CDCs. It is possible that the CDC-mediated platelet aggregation we observed in S. suis is a similar response mechanism to that used by a wide range of bacteria. These findings might lead to the discovery of potential therapeutic targets for S. suis-associated STSS.
Keywords: Ca2+ influx; Streptococcus suis (S. suis); platelet aggregation; streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS); suilysin (SLY).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suilysin-induced Platelet-Neutrophil Complexes Formation is Triggered by Pore Formation-dependent Calcium Influx.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 10;6:36787. doi: 10.1038/srep36787. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27830834 Free PMC article.
-
The genetically modified suilysin, rSLY(P353L), provides a candidate vaccine that suppresses proinflammatory response and reduces fatality following infection with Streptococcus suis.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 28;31(38):4209-15. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23856333
-
Acquiring high expression of suilysin enable non-epidemic Streptococccus suis to cause streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome (STSLS) through NLRP3 inflammasome hyperactivation.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):1309-1319. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1908098. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 33792531 Free PMC article.
-
Biological activities of suilysin: role in Streptococcus suis pathogenesis.Future Microbiol. 2016 Jul;11:941-54. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2016-0028. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Future Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27357518 Review.
-
Platelets, Bacterial Adhesins and the Pneumococcus.Cells. 2022 Mar 25;11(7):1121. doi: 10.3390/cells11071121. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Antibacterial and Antivirulence Activities of Floxuridine against Streptococcus suis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 18;24(18):14211. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814211. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762514 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 4 clonal complex 94 recovered from human and swine samples.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 27;18(7):e0288840. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288840. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37498866 Free PMC article.
-
Morin inhibits Listeria monocytogenes virulence in vivo and in vitro by targeting listeriolysin O and inflammation.BMC Microbiol. 2020 May 12;20(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01807-6. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32398085 Free PMC article.
-
An NLRP3 inflammasome-triggered cytokine storm contributes to Streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome (STSLS).PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jun 6;15(6):e1007795. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007795. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31170267 Free PMC article.
-
Amentoflavone Ameliorates Streptococcus suis-Induced Infection In Vitro and In Vivo.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 30;84(24):e01804-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01804-18. Print 2018 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30315078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvand M., Bhakdi S., Dahlbäck B., Preissner K. T. (1990). Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin attack on human platelets promotes assembly of the prothrombinase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 14377–14381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

