Rapid Modified QuEChERS Method for Pesticides Detection in Honey by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography UV-visible
- PMID: 27800334
- PMCID: PMC5083864
- DOI: 10.4081/ijfs.2014.1647
Rapid Modified QuEChERS Method for Pesticides Detection in Honey by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography UV-visible
Abstract
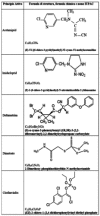
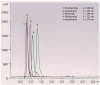
The extensive use of pesticides in agriculture plays an important role in bees die-off and allows the presence of residues in hive products, particularly in honey. An accurate and reliable analytical method, based on QuEChERS extractive technique, has been developed for the quantitative determination by high-performance liquid chromatography UV-visible detector of 5 pesticides (Deltamethrin, Dimethoate, Imidacloprid, Acetamiprid, Chlorfenvinphos) in honey. The method, according to Commission Directive 2002/63/EC and Regulation 882/2004/EC, provided excellent results with respect to linearity (correlation coefficient up to 0.993), limits of detection and quantification (0.005 and 0.01 µg/mL for Dimethoate, Deltamethrin and Chlorfenvinphos; 0.02 and 0.05 µg/mL for Acetamiprid and Imidacloprid), recovery values (86.4 to 96.3%), precision and relative expanded uncertainty of a measurement, demonstrating the conformity of the this method with the European directives. The proposed method was applied to 23 samples of Apulian honey. None of the investigated pesticides was detected in these samples.
Figures
References
-
- Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Stajnbaher D, Schenck FJ. 2003. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing Acetonitile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int 86:412-31. - PubMed
-
- AOAC, 2007. AOAC Official Method 2007.01 Pesticide residues in foods by Acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with Magnesium Sulfate gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Disponibile al sito: http://www.weber.hu/PDFs/QuEChERS/AOAC_2007_01.pdf - PubMed
-
- BSI, 2007. Food analysis. Determination of pesticide residues by LCtMS/MS-tandem mass spectrometric parameters. CEN/TS 15641. British Standards Institution ed., Londra, Gran Bretagna.
-
- BSI, 2008. Foods of plant origin. Determination of pesticide residues using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS following acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and clean-up by dispersive SPE-QuEChERS-method. BSI EN 15662:2008. British Standards Institution ed., Londra, Gran Bretagna.
-
- Commissione Europea, 1991. Direttiva del Consiglio del 15 luglio. 1991, relativa all’immissione in commercio dei prodotti fitosanitari, 91/414/CEE. In: Gazzetta ufficiale, L 230, 19/08/1991.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources