Surgical options for lumbar spinal stenosis
- PMID: 27801521
- PMCID: PMC6464992
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012421
Surgical options for lumbar spinal stenosis
Abstract
Background: Hospital charges for lumbar spinal stenosis have increased significantly worldwide in recent times, with great variation in the costs and rates of different surgical procedures. There have also been significant increases in the rate of complex fusion and the use of spinal spacer implants compared to that of traditional decompression surgery, even though the former is known to incur costs up to three times higher. Moreover, the superiority of these new surgical procedures over traditional decompression surgery is still unclear.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy of surgery in the management of patients with symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis and the comparative effectiveness between commonly performed surgical techniques to treat this condition on patient-related outcomes. We also aimed to investigate the safety of these surgical interventions by including perioperative surgical data and reoperation rates.
Search methods: Review authors performed electronic searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL, AMED, Web of Science, LILACS and three trials registries from their inception to 16 June 2016. Authors also conducted citation tracking on the reference lists of included trials and relevant systematic reviews.
Selection criteria: This review included only randomised controlled trials that investigated the efficacy and safety of surgery compared with no treatment, placebo or sham surgery, or with another surgical technique in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis.
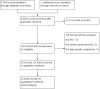
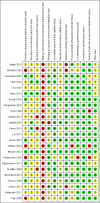
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers independently assessed the studies for inclusion and performed the 'Risk of bias' assessment, using the Cochrane Back and Neck Review Group criteria. Reviewers also extracted demographics, surgery details, and types of outcomes to describe the characteristics of included studies. Primary outcomes were pain intensity, physical function or disability status, quality of life, and recovery. The secondary outcomes included measurements related to surgery, such as perioperative blood loss, operation time, length of hospital stay, reoperation rates, and costs. We grouped trials according to the types of surgical interventions being compared and categorised follow-up times as short-term when less than 12 months and long-term when 12 months or more. Pain and disability scores were converted to a common 0 to 100 scale. We calculated mean differences for continuous outcomes and relative risks for dichotomous outcomes. We pooled data using the random-effects model in Review Manager 5.3, and used the GRADE approach to assess the quality of the evidence.
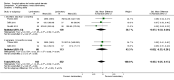
Main results: We included a total of 24 randomised controlled trials (reported in 39 published research articles or abstracts) in this review. The trials included 2352 participants with lumbar spinal stenosis with symptoms of neurogenic claudication. None of the included trials compared surgery with no treatment, placebo or sham surgery. Therefore, all included studies compared two or more surgical techniques. We judged all trials to be at high risk of bias for the blinding of care provider domain, and most of the trials failed to adequately conceal the randomisation process, blind the participants or use intention-to-treat analysis. Five trials compared the effects of fusion in addition to decompression surgery. Our results showed no significant differences in pain relief at long-term (mean difference (MD) -0.29, 95% confidence interval (CI) -7.32 to 6.74). Similarly, we found no between-group differences in disability reduction in the long-term (MD 3.26, 95% CI -6.12 to 12.63). Participants who received decompression alone had significantly less perioperative blood loss (MD -0.52 L, 95% CI -0.70 L to -0.34 L) and required shorter operations (MD -107.94 minutes, 95% CI -161.65 minutes to -54.23 minutes) compared with those treated with decompression plus fusion, though we found no difference in the number of reoperations (risk ratio (RR) 1.25, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.92). Another three trials investigated the effects of interspinous process spacer devices compared with conventional bony decompression. These spacer devices resulted in similar reductions in pain (MD -0.55, 95% CI -8.08 to 6.99) and disability (MD 1.25, 95% CI -4.48 to 6.98). The spacer devices required longer operation time (MD 39.11 minutes, 95% CI 19.43 minutes to 58.78 minutes) and were associated with higher risk of reoperation (RR 3.95, 95% CI 2.12 to 7.37), but we found no difference in perioperative blood loss (MD 144.00 mL, 95% CI -209.74 mL to 497.74 mL). Two trials compared interspinous spacer devices with decompression plus fusion. Although we found no difference in pain relief (MD 5.35, 95% CI -1.18 to 11.88), the spacer devices revealed a small but significant effect in disability reduction (MD 5.72, 95% CI 1.28 to 10.15). They were also superior to decompression plus fusion in terms of operation time (MD 78.91 minutes, 95% CI 30.16 minutes to 127.65 minutes) and perioperative blood loss (MD 238.90 mL, 95% CI 182.66 mL to 295.14 mL), however, there was no difference in rate of reoperation (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.32 to 1.51). Overall there were no differences for the primary or secondary outcomes when different types of surgical decompression techniques were compared among each other. The quality of evidence varied from 'very low quality' to 'high quality'.
Authors' conclusions: The results of this Cochrane review show a paucity of evidence on the efficacy of surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis, as to date no trials have compared surgery with no treatment, placebo or sham surgery. Placebo-controlled trials in surgery are feasible and needed in the field of lumbar spinal stenosis. Our results demonstrate that at present, decompression plus fusion and interspinous process spacers have not been shown to be superior to conventional decompression alone. More methodologically rigorous studies are needed in this field to confirm our results.
Conflict of interest statement
The review authors declare that they have no competing interests and received no external funding to perform this systematic review. GCM and MBP are supported by an international postgraduate research scholarship/postgraduate award from the Australian Department of Education and Training. CGM is supported by a principal research fellowship from the National Health and Medical Research Council. MLF is supported by a Sydney Medical Foundation Fellowship from the Sydney Medical School, The University of Sydney. BWK is co‐author of one of the included trials (Moojen 2013), but was not involved in the quality assessment or data extraction of this trial. The remaining authors have noting to declare.
Figures


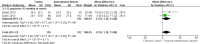








































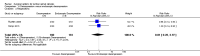
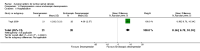
References
References to studies included in this review
Azzazi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Azzazi A, Elhawary Y. Dynamic stabilization using X‐stop versus transpedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar canal stenosis: comparative study of the clinical outcome. Neurosurgery Quartely 2010; Vol. 20:165‐9.
Bridwell 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Baldus C. The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. Journal of Spinal Disorders 1993;6:461‐72. - PubMed
Cavusoglu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cavusoglu H, Turkmenoglu O, Kaya RA, Tuncer C, Colak I, Sahin Y, et al. Efficacy of unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis. Turkish Neurosurgery 2007;17:100‐8. - PubMed
Celik 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Celik SE, Celik S, Goksu K, Kara A, Ince I. Microdecompressive laminatomy with a 5‐year follow‐up period for severe lumbar spinal stenosis. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques 2010;23:229‐35. - PubMed
Cho 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cho DY, Lin HL, Lee WY, Lee HC. Split‐spinous process laminotomy and discectomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a preliminary report. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2007;6:229‐39. - PubMed
Davis 2013 {published data only}
-
- Auerbach J, Davis R, Errico T, Bae H. Direct decompression and coflex interlaminar stabilization compared with laminectomy and posterior spinal fusion with pedicle screw instrumentation for spinal stenosis with back pain or degenerative spondylolisthesis: two‐year results from the prospective, randomized, multicenter FDA IDE trial. Spine Journal 2011;11:86S‐7S.
-
- Auerbach J, Zigler J, Davis R, Pettine K, Yeung A. Comparative cost‐effectiveness analysis of coflex interlaminar stabilization versus posterolateral fusion for lumbar stenosis and lowgrade spondylolisthesis. European Spine Journal 2012;21:S311‐2.
-
- Auerbach JD, Field JS. Two‐level Coflex interlaminar stabilization compared to two‐level lumbar spinal fusion for the treatment of spinal stenosis with low‐grade spondylolisthesis. Spine Journal 2013;13:155S‐6S.
-
- Auerbach JD, Schmier J, Ong KL, Lau E. Cost‐effectiveness of interlaminar stabilization compared with instrumented posterior spinal fusion for spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis. Spine Journal 2012;12:13S.
-
- Cano WG, Block JE, Haley T, Kuznits S, Miller LE. Lumbar spinal stenosis treatment with an interspinous spacer: preliminary results of a multicenter, randomized, controlled FDA‐IDE trial. PM&R 2011;3:S213.
Forsth 2016 {published data only}
-
- Forsth P, Olafsson G, Carlsson T, Frost A, Borgstrom F, Fritzell P, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of fusion surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2016;374:1413‐23. - PubMed
Ghogawala 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ghogawala Z, Benzel EC, Magge SN, Coumans JV, Harrington JF, Barker FG. Lumbar spinal fusion reduces risk of re‐operation after laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis associated with grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis: initial results from the SLIP trial. Neurosurgery 2010;67:542‐3.
-
- Ghogawala Z, Dziura J, Butler WE, Dai F, Terrin N, Magge SN, et al. Laminectomy plus fusion versus laminectomy alone for lumbar spondylolisthesis. New England Journal of Medicine 2016;374:1424‐34. - PubMed
Grob 1995 {published data only}
-
- Grob D, Humke T, Dvorak J. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Decompression with and without arthrodesis. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1995;77:1036‐41. - PubMed
-
- Grob D, Humke T, Dvorak J. [Significance of simultaneous fusion and surgical decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis]. Orthopade 1993;22:243‐9. - PubMed
Gurelik 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gurelik M, Bozkina C, Kars Z, Karadag O, Unal O, Bayrakli F. Unilateral laminotomy for decompression of lumbar stenosis is effective and safe: a prospective randomized comparative study. Journal of Neurological Sciences 2012;29:744‐53.
Hallett 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hallett A, Huntley JS, Gibson JN. Foraminal stenosis and single‐level degenerative disc disease: a randomized controlled trial comparing decompression with decompression and instrumented fusion. Spine 2007;32:1375‐80. - PubMed
Komp 2015 {published data only}
-
- Komp M, Hahn P, Oezdemir S, Giannakopoulos A, Heikenfeld R, Kasch R, et al. Bilateral spinal decompression of lumbar central stenosis with the full‐endoscopic interlaminar versus microsurgical laminotomy technique: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Pain Physician 2015;18:61‐70. - PubMed
Liu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Liu X, Yuan S, Tian Y. Modified unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: technical note. Spine 2013;38:E732‐7. - PubMed
Lonne 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lonne G, Johnsen LG, Aas E, Lydersen S, Andresen H, Ronning R, et al. Comparing cost‐effectiveness of X‐stop to minimally invasive decompression in lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:514‐20. - PubMed
-
- Lonne G, Johnsen LG, Rossvoll I, Andresen H, Storheim K, Zwart JA, et al. Minimally invasive decompression versus x‐stop in lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized controlled multicenter study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:77‐85. - PubMed
Mobbs 2014 {published data only}
-
- Mobbs RJ, Li J, Sivabalan P, Raley D, Rao PJ. Outcomes after decompressive laminectomy for lumbar spinal stenosis: comparison between minimally invasive unilateral laminectomy for bilateral decompression and open laminectomy. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2014;21:179‐86. - PubMed
Moojen 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Moojen WA, Arts MP, Jacobs WC, Zwet EW, Akker‐van Marle ME, Koes BW, et al. IPD without bony decompression versus conventional surgical decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: 2‐year results of a double‐blind randomized controlled trial. European Spine Journal 2015;24:2295‐305. - PubMed
-
- Akker‐van Marle ME, Moojen WA, Arts MP, Vleggeert‐Lankamp CL, Peul WC, Leiden‐The Hague Spine Intervention Prognostic Study Group. Interspinous process devices versus standard conventional surgical decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: cost utility analysis. Spine Journal 2016;16(6):702‐10. - PubMed
Postacchini 1993 {published data only}
-
- Postacchini F, Cinotti G, Perugia D, Gumina S. The surgical treatment of central lumbar stenosis. Multiple laminotomy compared with total laminectomy. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ British Volume 1993;75:386‐92. - PubMed
Rajasekaran 2013 {published data only}
-
- Rajasekaran S, Thomas A, Kanna R M, Shetty AP. Lumbar spinous process splitting decompression provides equivalent outcomes to conventional midline decompression in degenerative lumbar canal stenosis: a prospective, randomised controlled study of 51 patients. Spine 2013;38:1737‐43. - PubMed
Ruetten 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ruetten S, Komp M, Merk H, Godolias G. Surgical treatment for lumbar lateral recess stenosis with the full‐endoscopic interlaminar approach versus conventional microsurgical technique: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2009;10:476‐85. - PubMed
Stromqvist 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Stromqvist BH, Berg S, Gerdhem P, Johnsson R, Moller A, Sahlstrand T, et al. X‐stop versus decompressive surgery for lumbar neurogenic intermittent claudication: randomized controlled trial with 2‐year follow‐up. Spine 2013;38:1436‐42. - PubMed
Thome 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thome C, Schubert GA, Stier R, Hegewald AA, Schmiedek P. Long‐term outcome after less invasive surgery for decompression of lumbar stenosis ‐ a randomized comparison of unilateral laminotomy, bilateral laminotomy and laminectomy. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2010;113:A432‐3. - PubMed
-
- Thome C, Zevgaridis D, Leheta O, Bazner H, Pockler‐Schoniger C, Wohrle J, et al. Outcome after less‐invasive decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized comparison of unilateral laminotomy, bilateral laminotomy, and laminectomy. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2005;3:129‐41. - PubMed
Usman 2013 {published data only}
-
- Usman M, Ali M, Khanzada K, Ishaq M, Naeem ul Haq, Aman R, et al. Unilateral approach for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis: a minimal invasive surgery. Journal of the College of Physicians & Surgeons Pakistan 2013;23:852‐6. - PubMed
Watanabe 2011 {published data only}
-
- Watanabe K, Matsumoto M, Ikegami T, Nishiwaki Y, Tsuji T, Ishii K, et al. Reduced postoperative wound pain after lumbar spinous process‐splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis: a randomized controlled study. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2011;14:51‐8. - PubMed
Yagi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yagi M, Okada E, Ninomiya K, Kihara M. Postoperative outcome after modified unilateral‐approach microendoscopic midline decompression for degenerative spinal stenosis. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2009;10:293‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abdu 2009 {published data only}
Altaf 2011 {published data only}
-
- Altaf F, Jalgaonkar A, Raman SA. Prospective study of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine Journal 2011;11:112S‐3S.
Andersen 2008 {published data only}
Anderson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Anderson DG, Patel A, Maltenfort M, Vaccaro AR, Ratliff J, Hilibrand A, et al. Lumbar decompression using a traditional midline Approach versus a tubular retractor system: comparison of patient‐based clinical outcomes. Spine 2011;36:E320‐5. - PubMed
Aoki 2012 {published data only}
-
- Aoki Y, Yamagata M, Ikeda Y, Nakajima F, Ohtori S, Nakagawa K, et al. A prospective randomized controlled study comparing transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion techniques for degenerative spondylolisthesis: unilateral pedicle screw and 1 cage versus bilateral pedicle screws and 2 cages. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2012;17:153‐9. - PubMed
Arriagada 2000 {published data only}
-
- Arriagada LO. Manejo quirúrgico con instrumentación transpedicular de la espondilolistesis. Revista Chilena de Neurocirugía 2000;15:29‐36.
Asazuma 2004 {published data only}
-
- Asazuma T, Yamugishi M, Sato M, Ichimura S, Fujikawa K, Crock HV. Posterior spinal fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases using the Crock‐Yamagishi (C‐Y) spinal fixation system. Journal of Spinal Disorders and Techniques 2004;17:174‐7. - PubMed
Auerbach 2011 {published data only}
-
- Auerbach J, Davis R. Direct versus indirect decompression and stabilization: a comparison of clinical outcomes with coflex interlaminar stabilization, laminectomy and spinal fusion, and X‐STOP to treat spinal stenosis and low‐grade degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine Journal 2011;11:104S‐5S.
Auerbach 2012 {published data only}
-
- Auerbach J, McGowan K, Halevi M, Maislin G. Mitigating the potential for adverse event reporting bias: utilization of an independent clinical events committee. European Spine Journal 2012;21:S284.
Bazan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bazan O. Estenosis del conducto raquideo lumbar: artrodesis posterolateral. Revista de la Asociacion Argentina de Ortopedia y Traumatologia 2002;67:296.
Benli 2006 {published data only}
-
- Benli I T, Cicek H, Kaya A. Comparison of sagittal plane realignment and reduction with posterior instrumentation in developmental low or high dysplastic spondylolisthesis. Kobe Journal of Medical Sciences 2006;52:151‐69. - PubMed
Bjarke 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bjarke Christensen F, Stender Hansen E, Laursen M, Thomsen K, Bunger CE. Long‐term functional outcome of pedicle screw instrumentation as a support for posterolateral spinal fusion: randomized clinical study with a 5‐year follow‐up. Spine 2002;27:1269‐77. - PubMed
Blumenthal 2013 {published data only}
-
- Blumenthal C, Curran J, Benzel EC, Potter R, Magge SN, Harrington Jr JF, et al. Radiographic predictors of delayed instability following decompression without fusion for degenerative Grade I lumbar spondylolisthesis: clinical article. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2013;18:340‐6. - PubMed
Bresnahan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bresnahan L, Ogden AT, Natarajan RN, Fessler RG. A biomechanical evaluation of graded posterior element removal for treatment of lumbar stenosis: comparison of a minimally invasive approach with two standard laminectomy techniques. Spine 2009;34:17‐23. - PubMed
Cakir 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cakir B, Carazzo C, Schmidt R, Mattes T, Reichel H, Käfer W. Adjacent segment mobility after rigid and semirigid instrumentation of the lumbar spine. Spine 2009;34:1287‐91. - PubMed
Cannone 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cannone J. Spinal Stenosis and Fusion Surgery. Positive Health 2010;175:1.
Carragee 1997 {published data only}
-
- Carragee EJ. Single‐level posterolateral arthrodesis, with or without posterior decompression, for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. A prospective, randomized study. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American volume 1997; Vol. 79:1175‐80. - PubMed
Carrasco 1986 {published data only}
-
- Carrasco M, Simonovich Z. Conducto raquídeo estrechado. Revista de la Asociación Argentina de Ortopedia y Traumatología 1986;51:349‐62.
Carreon 2009 {published data only}
-
- Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Djurasovic M, Campbell MJ, Puno RM, Johnson JR, et al. RhBMP‐2 versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar spine fusion in patients over 60 years of age: a cost‐utility study. Spine 2009;34:238‐43. - PubMed
Cassinelli 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cassinelli EH, Eubanks J, Vogt M, Furey C, Yoo J, Bohlman HH. Risk factors for the development of perioperative complications in elderly patients undergoing lumbar decompression and arthrodesis for spinal stenosis: an analysis of 166 patients. Spine 2007;32:230‐5. - PubMed
Chen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chen KX, Yang QY, Liu XC, Li HJ. [Treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis through posterolateral fusion and fixation with pedicle screws]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010; Vol. 23:254‐6. - PubMed
Cheng 2009 {published data only}
Choi 2009 {published data only}
Dahdaleh 2013 {published data only}
-
- Dahdaleh NS, Nixon AT, Lawton CD, Wong AP, Smith ZA, Fessler RG. Outcome following unilateral versus bilateral instrumentation in patients undergoing minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a single‐center randomized prospective study. Neurosurgical Focus 2013;35:E13. - PubMed
Dantas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Dantas FL, Prandini MN, Ferreira MA. Comparison between posterior lumbar fusion with pedicle screws and posterior lumbar interbody fusion with pedicle screws in adult spondylolisthesis. Arquivos de Neuropsiquiatria 2007; Vol. 65:764‐70. - PubMed
Delank 2002 {published data only}
-
- Delank KS, Eysel P, Zollner J, Drees P, Nafe B, Rompe JD. Undercutting decompression versus laminectomy. Clinical and radiological results of a prospective controlled trial. Orthopade 2002;31:1048‐56. - PubMed
Delawi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Delawi D, Dhert WJ, Rillardon L, Gay E, Prestamburgo D, Garcia‐Fernandez C, et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter study of osteogenic protein‐1 in instrumented posterolateral fusions: report on safety and feasibility. Spine 2010;35:1185‐91. - PubMed
Desai 2012 {published data only}
-
- Desai A, Bekelis K, Ball P, Lurie J, Mirza S, Tosteson TD, et al. Variability in outcomes after surgery for spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery 2012;71:E545.
Dimar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dimar Ii JR, Glassman SD, Burkus JK, Pryor PW, Hardacker JW, Carreon LY. Clinical and radiographic analysis of an optimized rhBMP‐2 formulation as an autograft replacement in posterolateral lumbar spine arthrodesis. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 2009;91:1377‐86. - PubMed
Dirisio 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dirisio DJ, Regan JJ, Hartjen CA, Dryer RF, Rodgers WB, Pettine K, et al. Treatment of 110 symptomatic lumbar stenosis patients at 16 centers in an FDA IDE study. Journal of Neurosurgery 2011;115:A408‐9.
Dryer 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dryer R, Youssef JA, Lorio MP, DiRisio DJ, Myer J, Baker K. Acadia facet replacement system ide clinical trial: preliminary two‐year outcomes. Spine Journal 2012;12:140S‐1S.
Epstein 2006 {published data only}
-
- Epstein NE. A preliminary study of the efficacy of Beta Tricalcium Phosphate as a bone expander for instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusions. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques 2006;19:424‐9. - PubMed
Escobar 2003 {published data only}
-
- Escobar E, Transfeldt E, Garvey T, Ogilvie J, Graber J, Schultz L. Video‐assisted versus open anterior lumbar spine fusion surgery: a comparison of four techniques and complications in 135 patients. Spine 2003;28:729‐32. - PubMed
Fan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Fan J, Yu GR, Liu F, Zhao J, Zhao WD. Biomechanical changes of modified Scott wiring fixation in treating 12 young patients with lumbar spondylolysis. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 2009;13:4245‐8.
Fast 1985 {published data only}
-
- Fast A, Robin GC, Floman Y. Surgical treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 1985;66:149‐51. - PubMed
Feng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Feng ZZ, Cao YW, Jiang C, Jiang XX. Short‐term outcome of bilateral decompression via a unilateral paramedian approach for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw fixation. Orthopedics 2011;34:364. - PubMed
Fitzgerald 1976 {published data only}
-
- Fitzgerald JA, Newman PH. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ British Volume 1976;58:184‐92. - PubMed
Försth 2013 {published data only}
-
- Försth P, Michaëlsson K, Sandén B. Does fusion improve the outcome after decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis?: A two‐year follow‐up study involving 5390 patients. Bone & Joint Journal 2013;95‐B:960‐5. - PubMed
Fu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fu YS, Zeng BF, Xu JG. Long‐term outcomes of two different decompressive techniques for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine 2008;33:514‐8. - PubMed
Fujiya 1990 {published data only}
-
- Fujiya M, Saita M, Kaneda K, Abumi K. Clinical study on stability of combined distraction and compression rod instrumentation with posterolateral fusion for unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 1990;15:1216‐22. - PubMed
Ghahreman 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ghahreman A, Ferch RD, Rao PJ, Bogduk N. Minimal access versus open posterior lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery 2010; Vol. 66:296‐304. - PubMed
González 1992 {published data only}
-
- González AG, Espinosa ES. Tratamiento quirúrgico del conducto lumbar estrecho degenerativo. Revista Mexicana de Ortopedia y Traumatología 1992;6:214‐6.
Gotfryd 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gotfryd AO, Henriques GG, Poletto PR. Influência da extensão da artrodese lombossacra nos resultados clínicos e funcionais. Coluna/Columna 2012;11:13‐6.
Gotfryd 2012a {published data only}
-
- Gotfryd AO, Spolidoro DR, Poletto PR. Descompressão neural isolada ou associada à fusão póstero‐lateral nas afecções degenerativas lombossacras: avaliação da qualidade de vida e incapacidade funcional pós‐operatória. Coluna/Columna 2012;11:17‐20.
Gu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gu Y, Chen L, Yang HL, Chen XQ, Dong RB, Han GS, et al. Efficacy of surgery and type of fusion in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2009;16:1291‐5. - PubMed
Haley 2012 {published data only}
-
- Haley TR, Dankmyer C, Miller LE, Block J. Novel interspinous spacer for treatment of moderate lumbar spinal stenosis: 1‐year results of a randomized controlled IDE trial. Pain Medicine 2012;13:305‐6.
Haley 2012a {published data only}
-
- Haley TR, Lichten D, Miller LE. Prospective randomized controlled trial of interspinous spacer treatment for moderate lumbar spinal stenosis. Pain Medicine 2012;13:1101.
Halm 2010 {published data only}
-
- Halm HFH, Richter A. Microsurgical decompression vs. microsurgical decompression plus interspinous stabilization in lumbar spinal stenosis. A prospective comparison of 60 patients. Spine Journal 2010; Vol. 10:S66.
Herkowitz 1991 {published data only}
-
- Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 1991; Vol. 73:802‐8. - PubMed
Hong 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hong SW, Lee HY, Kim KH, Lee SH. Interspinous ligamentoplasty in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis: Midterm clinical results. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2010;13:27‐35. - PubMed
Hong 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hong SW, Choi KY, Ahn Y, Baek OK, Wang JC, Lee SH, et al. A comparison of unilateral and bilateral laminotomies for decompression of L4‐L5 spinal stenosis. Spine 2011;36:E172‐8. - PubMed
Hwang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hwang CJ, Vaccaro AR, Hong J, Lawrence JP, Fischgrund JS, Alaoui‐Ismaili MH, et al. Immunogenicity of osteogenic protein 1: results from a prospective, randomized, controlled, multicenter pivotal study of uninstrumented lumbar posterolateral fusion. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 2010;13:484‐93. - PubMed
Ikuta 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ikuta K, Arima J, Tanaka T, Oga M, Nakano S, Sasaki K, et al. Short‐term results of microendoscopic posterior decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis. Technical note. Journal of Neurosurgery Spine 2005;2:624‐33. - PubMed
Imagama 2009 {published data only}
-
- Imagama S, Kawakami N, Matsubara Y, Kanemura T, Tsuji T, Ohara T. Preventive effect of artificial ligamentous stabilization on the upper adjacent segment impairment following posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 2009;34:2775‐81. - PubMed
Ito 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ito Z, Matsuyama Y, Sakai Y, Imagama S, Wakao N, Ando K, et al. Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 2010;35:E1101‐5. - PubMed
Katz 1997 {published data only}
-
- Katz JN, Lipson SJ, Lew RA, Grobler LJ, Weinstein JN, Brick GW, et al. Lumbar laminectomy alone or with instrumented or noninstrumented arthrodesis in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Patient selection, costs, and surgical outcomes. Spine 1997;22:1123‐31. - PubMed
Kawaguchi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Kanamori M, Ishihara H, Kikkawa T, Matsui H, Tsuji H, et al. Clinical and radiographic results of expansive lumbar laminoplasty in patients with spinal stenosis. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 2004;86A:292‐9. - PubMed
Kim 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kim KT, Lee SH, Lee YH, Bae SC, Suk KS. Clinical outcomes of 3 fusion methods through the posterior approach in the lumbar spine. Spine 2006;31:1351‐7. - PubMed
Kim 2007 {published data only}
Kim 2007a {published data only}
-
- Kim SW, Ju CI, Kim CG, Lee SM, Shin H. Minimally invasive lumbar spinal decompression: A comparative study between bilateral laminotomy and unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression. Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society 2007;42:195‐9.
Konno 2000 {published data only}
-
- Konno S, Kikuchi S. Prospective study of surgical treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison between decompression alone and decompression with Graf system stabilization. Spine 2000;25:1533‐7. - PubMed
Kornblum 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kornblum MB, Fischgrund JS, Herkowitz HN, Abraham DA, Berkower DL, Ditkoff JS. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long‐term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Spine 2004;29:726‐33; discussion 733‐4. - PubMed
Korovessis 2004 {published data only}
-
- Korovessis P, Papazisis Z, Koureas G, Lambiris E. Rigid, semirigid versus dynamic instrumentation for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a correlative radiological and clinical analysis of short‐term results. Spine 2004; Vol. 29:735‐42. - PubMed
Ledonio 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ledonio CGT, Polly DW, Ghogawala Z, Rampersaud RY, Santos ERG, Sembrano JN, et al. Societal cost impact of decompression alone versus decompression and fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine Journal 2012;12:125S‐6S.
Lee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lee SC, Chen JF, Wu CT, Lee ST. In situ local autograft for instrumented lower lumbar or lumbosacral posterolateral fusion. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2009;16:37‐43. - PubMed
Lian 2010 {published data only}
Liao 2011 {published data only}
-
- Liao JC, Chen WJ, Chen LH, Niu CC, Keorochana G. Surgical outcomes of degenerative spondylolisthesis with L5‐S1 disc degeneration: comparison between lumbar floating fusion and lumbosacral fusion at a minimum 5‐year follow‐up. Spine 2011;36:1600‐7. - PubMed
Mahir 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mahir S, Marsh G. The 3 year results of a prospective randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy with the dynamic stabilisation of Wallis ligament as an interspinus implant in lumbar spine decompression. European Spine Journal 2012;21:S262. - PubMed
McConnell 2011 {published data only}
-
- McConnell J. A comparison of ß‐TCP+BMA versus RhBMP‐2 in anterior lumbar interbody fusion: a prospective, randomized trial with two‐year clinical and radiographic outcomes. Spine Journal 2011;11:64S‐5S.
Michielsen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Michielsen J, Sys J, Rigaux A, Bertrand C. The effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein‐2 in single‐level posterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 2013;95:873‐80. - PubMed
Pappas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pappas CTE, Sonntag VKH. Lumbar stenosis in the elderly. Neurosurgery Quarterly 1994;4:102‐12.
Parker 2013 {published data only}
-
- Parker SL, Adogwa O, Davis BJ, Fulchiero E, Aaronson O, Cheng J, et al. Cost‐utility analysis of minimally invasive versus open multilevel hemilaminectomy for lumbar stenosis. Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques 2013;26:42‐7. - PubMed
Radcliff 2011 {published data only}
Radcliff 2012 {published data only}
-
- Radcliff K, Hwang R, Hilibrand A, Smith HE, Gruskay J, Lurie JD, et al. The effect of iliac crest autograft on the outcome of fusion in the setting of degenerative spondylolisthesis: a subgroup analysis of the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT). Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ Series A 2012;94:1685‐92. - PMC - PubMed
Rapp 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rapp SM. Decompression for stenosis less costly than fusion, especially when instrumented. Orthopedics Today 2009;29:38.
Rapp 2011 {published data only}
-
- Rapp SM. Greater spondylolisthesis pain relief found with bilateral vs. unilateral pedicle screws. Orthopedics Today 2011;31:61.
Repantis 2009 {published data only}
-
- Repantis T, Korovessis P, Papazisis Z. Effect of sagittal spinal alignment on low back pain following decompression and stabilisation with dynamic, semirigid and rigid instrumentation. A multifactorial analysis. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ British Volume 2009; Vol. 91:149.
Richter 2010 {published data only}
Rompe 1995 {published data only}
-
- Rompe JD, Eysel P, Hopf C, Heine J. Surgical management of central lumbar spinal stenosis ‐ results with decompressive laminectomy only and with concomitant instrumented fusion with the Cotrel‐Dubousset‐instrumentation. Neuro‐Orthopedics 1995; Vol. 19:17‐31.
Rosa 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rosa FWF, Foizer GA, Yoshino CV, Yonezaki AM, Ueno FH, Valesin Filho ES, et al. Avaliação dos pacientes submetidos à descompressão e artrodese póstero‐lateral devido à espondilolistese degenerativa com dois anos de acompanhamento. Coluna/Columna 2012;11:200‐3.
Rowland 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rowland KA. Spinal stenosis: new study purports to show surgery better than medical management. Evidence‐Based Practice 2009;12:1‐3.
Satomi 1992 {published data only}
-
- Satomi K, Hirabayashi K, Toyama Y, Fujimura Y. A clinical study of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Radiographic analysis and choice of treatment. Spine 1992;17:1329‐36. - PubMed
Schnake 2006 {published data only}
-
- Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 2006;31:442‐9. - PubMed
Sears 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sears WR, Davis RJ, Auerbach JD. The Coflex versus fusion US FDA IDE trial: an in vivo biomechanical study of adjacent segment motion following fusion. Spine Journal 2012;12:29S.
Sengupta 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sengupta DK, Truumees E, Patel CK, Kazmierczak C, Hughes B, Elders G, et al. Outcome of local bone versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft in the instrumented posterolateral fusion of the lumbar spine. Spine 2006;31:985‐91. - PubMed
Shapiro 2005 {published data only}
-
- Shapiro S, Rodgers RB, Sloan R, Altstadt T, Miller J. A randomized trial of instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion using machined cortical wedges/local bone with or without rhBMP2 in the treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with stenosis. Neurosurgery 2005;57:398.
Skidmore 2011 {published data only}
-
- Skidmore G, Ackerman SJ, Bergin C, Ross D, Butler J, Suthar M, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of the X‐STOP interspinous spacer for lumbar spinal stenosis: a comparison with conservative care and laminectomy. Spine 2011;36:E345‐56. - PubMed
Smoljanovic 2010 {published data only}
-
- Burkus JK, Gornet MF, Schuler TC, Kleeman TJ, Zdeblick TA. Six‐year outcomes of anterior lumbar interbody arthrodesis with use of interbody fusion cages and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein‐2. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 2009;91:1181‐9. - PubMed
Smorgick 2013 {published data only}
Steffee 1993 {published data only}
-
- Steffee AD, Brantigan JW. The variable screw placement spinal fixation system. Report of a prospective study of 250 patients enrolled in Food and Drug Administration clinical trials. Spine 1993;18:1160‐72. - PubMed
Tani 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tani T, Ushida T, Ishida K, Iai H, Noguchi T, Yamamoto H. Relative safety of anterior microsurgical decompression versus laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy with a massive ossified posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine 2002;27:2491‐8. - PubMed
Tenhula 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tenhula J, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Gupta P, Riew D. Prospective functional evaluation of the surgical treatment of neurogenic claudication in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Journal of Spinal Disorders 2000;13:276‐82. - PubMed
Tsutsumimoto 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M, Ohta H, Misawa H. Mini‐open versus conventional open posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison of paraspinal muscle damage and slip reduction. Spine 2009;34:1923‐8. - PubMed
Valesin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Valesin Filho ES, Ueno FH, Cabral LTB, Yonezaki AM, Nicolau RJ, Rodrigues LMR. Estudo prospectivo de avaliação de dor e incapacidade de pacientes operados de estenose de canal lombar com seguimento mínimo de dois anos. Coluna/Columna 2009;8:390‐4.
Videbaek 2010 {published data only}
-
- Videbaek TS, Egund N, Christensen FB, Grethe Jurik A, Bunger CE. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal fusion: the impact of anterior column support: a randomized clinical trial with an eight‐ to thirteen‐year magnetic resonance imaging follow‐up. Spine 2010;35:1955‐64. - PubMed
Wang 1998 {published data only}
-
- Wang PJ, Chen WJ, Chen LH, Niu CC. Spinal fusion and pedicle screw instrumentation in the treatment of spondylolisthesis over the age of 60. Changgeng Yi Xue Za Zhi 1998;21:436‐41. - PubMed
Weinstein 2007 {published data only}
Whang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Whang PG, Patel VV, Bradley WD, Block JE. Midterm outcomes of a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial comparing the clinical efficacy of interspinous spacers as a treatment for moderate lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine Journal 2013;13:136S‐7S.
Willén 2008 {published data only}
-
- Willén J, Wessberg PJ, Danielsson B. Surgical results in hidden lumbar spinal stenosis detected by axial loaded computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: an outcome study. Spine 2008;33:E109‐15. - PubMed
Xiao 2007 {published data only}
-
- Xiao R, Li Q, Tang Z. [Comparative study of lumbar spondylolisthesis treated by three different materials]. Chinese Journal of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery 2007; Vol. 21:453‐6. - PubMed
Xiao 2007a {published data only}
-
- Xiao RC, Xiao ZM, Li Q, Tang ZH, Hu JZ, Zou GY. Bone morphogenetic protein and interbody fusion cage change the height of intervertebral space in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 2007;11:1443‐6.
Yamada 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yamada T, Yoshii T, Sotome S, Yuasa M, Kato T, Arai Y, et al. Hybrid grafting using bone marrow aspirate combined with porous β‐tricalcium phosphate and trephine bone for lumbar posterolateral spinal fusion: a prospective, comparative study versus local bone grafting. Spine 2012;37:E174‐9. - PubMed
Yang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yang B, Chen R, Xie P, Liu B, Dong J, Rong L. [Microendoscopic decompression via unilateral approach for lumbar spinal stenosis]. Chung‐Kuo Hsiu Fu Chung Chien Wai Ko Tsa Chih/Chinese Journal of Reparative & Reconstructive Surgery 2011;25:1158‐63. - PubMed
Yu 2008 {published data only}
Zdeblick 1993 {published data only}
-
- Zdeblick TA. A prospective, randomized study of lumbar fusion. Preliminary results. Spine 1993;18:983‐91. - PubMed
Zucherman 2004 {published data only}
Additional references
Abumi 1990
-
- Abumi K, Panjabi MM, Kramer KM, Duranceau J, Oxland T, Crisco JJ. Biomechanical evaluation of lumbar spinal stability after graded facetectomies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1990;15:1142‐7. - PubMed
Arnoldi 1976
-
- Arnoldi CC, Brodsky AE, Cauchoix J, Crock HV, Dommisse GF, Edgar MA, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis and nerve root entrapment syndromes. Definition and classification. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 1976;115:4‐5. - PubMed
Aryanpur 1988
-
- Aryanpur J, Ducker T. Multilevel lumbar laminotomies for focal spinal stenosis: case report. Neurosurgery 1988;23:111‐5. - PubMed
Bailey 1911
-
- Bailey P, Casamajor L. Osteo‐arthritis of the spine as a cause of compression of the spinal cord and its roots: with report of five cases. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1911;38:588‐609.
Blau 1961
-
- Blau JN, Logue V. Intermittent claudication of the cauda equina: an unusual syndrome resulting from central protrusion of a lumbar intervertebral disc. Lancet 1961;277:1081‐6.
Boden 1990
-
- Boden SD, Davis DO, Dina TS, Patronas NJ, Wiesel SW. Abnormal magnetic‐resonance scans of the lumbar spine in asymptomatic subjects. A prospective investigation. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery ‐ American Edition 1990;72:403‐8. - PubMed
Buchbinder 2009
-
- Buchbinder R, Osborne RH, Ebeling PR, Wark JD, Mitchell P, Wriedt C, et al. A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361:557‐68. - PubMed
Chou 2011
Cooper 1991
-
- Cooper RG, Mitchell WS, Illingworth KJ, Forbes WS, Gillespie JE, Jayson MI. The role of epidural fibrosis and defective fibrinolysis in the persistence of postlaminectomy back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991;16:1044‐8. - PubMed
Delitto 2015
Deyo 2010
Deyo 2013
Flum 2006
-
- Flum DR. Interpreting surgical trials with subjective outcomes: avoiding UnSPORTsmanlike conduct. JAMA 2006;296:2483‐5. - PubMed
Furlan 2015
-
- Furlan AD, Malmivaara A, Chou R, Maher CG, Deyo RA, Schoene M, et al. 2015 Updated Method Guideline for Systematic Reviews in the Cochrane Back and Neck Group. Spine 2015; Vol. 40, issue 21:1660‐73. - PubMed
Gibson 2005
-
- Gibson JN, Waddell G. Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis: updated Cochrane Review. Spine 2005;30:2312‐20. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines: 6. Rating the quality of evidence‐‐imprecision. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:1283‐93. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Hopp 1988
-
- Hopp E, Tsou PM. Postdecompression lumbar instability. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 1988;227:143‐51. - PubMed
Horng 2003
-
- Horng S, Miller FG. Ethical framework for the use of sham procedures in clinical trials. Critical Care Medicine 2003;31:S126‐30. - PubMed
Ioannidis 2004
-
- Ioannidis JP, Evans SJ, Gotzsche PC, O'Neill RT, Altman DG, Schulz K, et al. Better reporting of harms in randomized trials: an extension of the CONSORT statement. Annals of Internal Medicine 2004;141:781‐8. - PubMed
Ishimoto 2013
-
- Ishimoto Y, Yoshimura N, Muraki S, Yamada H, Nagata K, Hashizume H, et al. Associations between radiographic lumbar spinal stenosis and clinical symptoms in the general population: the Wakayama Spine Study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2013;21:783‐8. - PubMed
Jansson 2003
Kalichman 2009
Katz 2008
-
- Katz JN, Harris MB. Clinical practice. Lumbar spinal stenosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358:818‐25. - PubMed
Kawaguchi 1996
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. A histologic and enzymatic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996;21:941‐4. - PubMed
Kovacs 2011
-
- Kovacs FM, Urrútia G, Alarcón JD. Surgery versus conservative treatment for symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Spine 2011;36:E1335‐51. - PubMed
Lane 1893
-
- Lane A. Case of spondylolisthesis associated with progressive paraplegia; laminectomy. Lancet 1893;1:991‐2.
Lee 1983
-
- Lee CK. Lumbar spinal instability (olisthesis) after extensive posterior spinal decompression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1983;8:429‐33. - PubMed
Machado 2015
May 2013
-
- May S, Comer C. Is surgery more effective than non‐surgical treatment for spinal stenosis, and which non‐surgical treatment is more effective? A systematic review. Physiotherapy 2013;99:12‐20. - PubMed
Meyerding 1932
-
- Meyerding HW. Spondylolisthesis. Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics 1932;54:37‐377.
Moojen 2011
Overdevest 2015
-
- Overdevest GM, Jacobs W, Vleggeert‐Lankamp C, Thome C, Gunzburg R, Peul W. Effectiveness of posterior decompression techniques compared with conventional laminectomy for lumbar stenosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010036.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Portal 1803
-
- Portal A. Cours d'anatomie médicale, ou éléments de l'anatomie de l'homme. 1. Paris: Baudouin, 1803.
Review Manager [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schulz 2010
See 1975
-
- See DH, Kraft GH. Electromyography in paraspinal muscles following surgery for root compression. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1975;56:80‐3. - PubMed
Senegas 1991
-
- Senegas J. [Surgery of the intervertebral ligaments, alternative to arthrodesis in the treatment of degenerative instabilities]. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica 1991;57 Suppl 1:221‐6. - PubMed
Siebert 2009
-
- Siebert E, Pruss H, Klingebiel R, Failli V, Einhaupl KM, Schwab JM. Lumbar spinal stenosis: syndrome, diagnostics and treatment. Nature Reviews Neurology 2009;5:392‐403. - PubMed
Smith 1829
-
- Smith AG. Account of a case in which portions of three dorsal vertebrae were removed for the relief of paralysis from fracture, with partial success. North American Medical and Surgical Journal 1829;8:94‐7.
Spetzger 1997
-
- Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Naujokat C, Keyserlingk DG, Gilsbach JM. Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part I: Anatomical and surgical considerations. Acta Neurochirurgica 1997;139:392‐6. - PubMed
Spetzger 1997a
-
- Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Reinges MHT, Gilsbach JM. Unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. Part II: Clinical experiences. Acta Neurochirurgica 1997;139:397‐403. - PubMed
Taylor 1994
-
- Taylor VM, Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Kreuter W. Low back pain hospitalization. Recent United States trends and regional variations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1994;19:1207‐12; discussion 13. - PubMed
Wartolowska 2014
Watanabe 2005
-
- Watanabe K, Hosoya T, Shiraishi T, Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Toyama Y. Lumbar spinous process‐splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis. Technical note. Journal of Neurosurgery Spine 2005;3:405‐8. - PubMed
Weinstein 2008
Wu 2014
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

