Fitness costs restrict niche expansion by generalist niche-constructing pathogens
- PMID: 27801902
- PMCID: PMC5270578
- DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2016.137
Fitness costs restrict niche expansion by generalist niche-constructing pathogens
Abstract
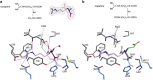
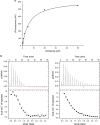
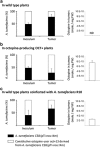
We investigated the molecular and ecological mechanisms involved in niche expansion, or generalism, versus specialization in sympatric plant pathogens. Nopaline-type and octopine-type Agrobacterium tumefaciens engineer distinct niches in their plant hosts that provide different nutrients: nopaline or octopine, respectively. Previous studies revealed that nopaline-type pathogens may expand their niche to also assimilate octopine in the presence of nopaline, but consequences of this phenomenon on pathogen dynamics in planta were not known. Here, we provided molecular insight into how the transport protein NocT can bind octopine as well as nopaline, contributing to niche expansion. We further showed that despite the ability for niche expansion, nopaline-type pathogens had no competitive advantage over octopine-type pathogens in co-infected plants. We also demonstrated that a single nucleotide polymorphism in the nocR gene was sufficient to allow octopine assimilation by nopaline-type strains even in absence of nopaline. The evolved nocR bacteria had higher fitness than their ancestor in octopine-rich transgenic plants but lower fitness in tumors induced by octopine-type pathogens. Overall, this work elucidates the specialization of A. tumefaciens to particular opine niches and explains why generalists do not always spread despite the advantage associated with broader nutritional niches.
Figures


References
-
- Abrams PA. (2006). The prerequisites for and likelihood of generalist-specialist coexistence. Am Nat 167: 329–342. - PubMed
-
- Abrams PA. (2012). The eco-evolutionary responses of a generalist consumer to resource competition. Evolution 66: 3130–3143. - PubMed
-
- Akakura R, Winans SC. (2002). Constitutive mutations of the OccR regulatory protein affect DNA bending in response to metabolites released from plant tumors. J Biol Chem 277: 5866–5874. - PubMed
-
- Blanc E, Roversi P, Vonrhein C, Flensburg C, Lea SM, Bricogne G. (2004). Refinement of severely incomplete structures with maximum likelihood in BUSTER-TNT. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60: 2210–2221. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

