Neural specificity of the RNA-binding protein Elav is achieved by post-transcriptional repression in non-neural tissues
- PMID: 27802174
- PMCID: PMC5201049
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.141978
Neural specificity of the RNA-binding protein Elav is achieved by post-transcriptional repression in non-neural tissues
Erratum in
-
Correction: Neural specificity of the RNA-binding protein Elav is achieved by post-transcriptional repression in non-neural tissues.Development. 2017 Apr 15;144(8):1578. doi: 10.1242/dev.151753. Development. 2017. PMID: 28400435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
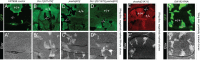
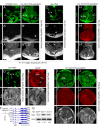
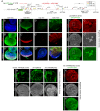
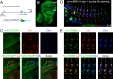
Drosophila Elav is the founding member of the conserved family of Hu RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), which play crucial and diverse roles in post-transcriptional regulation. Elav has long served as the canonical neuronal marker. Surprisingly, although Elav has a well-characterized neural cis-regulatory module, we find endogenous Elav is also ubiquitously transcribed and post-transcriptionally repressed in non-neural settings. Mutant clones of multiple miRNA pathway components derepress ubiquitous Elav protein. Our re-annotation of the elav transcription unit shows not only that it generates extended 3' UTR isoforms, but also that its universal 3' UTR isoform is much longer than previously believed. This longer common 3' UTR includes multiple conserved, high-affinity sites for the miR-279/996 family. Of several miRNA mutants tested, endogenous Elav and a transgenic elav 3' UTR sensor are derepressed in mutant clones of mir-279/996 We also observe cross-repression of Elav by Mei-P26, another RBP derepressed in non-neural miRNA pathway clones. Ubiquitous Elav has regulatory capacity, since derepressed Elav can stabilize an Elav-responsive sensor. Repression of Elav in non-neural territories is crucial as misexpression here has profoundly adverse consequences. Altogether, we define unexpected post-transcriptional mechanisms that direct appropriate cell type-specific expression of a conserved neural RBP.
Keywords: Drosophila; Elav; Mei-P26; MicroRNA; Neuron; RNA-binding protein.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ELAV/Hu RNA binding proteins determine multiple programs of neural alternative splicing.PLoS Genet. 2021 Apr 7;17(4):e1009439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009439. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33826609 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping Activities of ELAV/Hu Family RNA Binding Proteins Specify the Extended Neuronal 3' UTR Landscape in Drosophila.Mol Cell. 2020 Oct 1;80(1):140-155.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.007. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33007254 Free PMC article.
-
ELAV mediates 3' UTR extension in the Drosophila nervous system.Genes Dev. 2012 Oct 15;26(20):2259-64. doi: 10.1101/gad.199653.112. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 23019123 Free PMC article.
-
ELAV proteins along evolution: back to the nucleus?Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:447-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23439364 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal RNA signatures by ELAV/Hu proteins.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Mar;14(2):e1733. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1733. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 35429136 Review.
Cited by
-
A nonneural miRNA cluster mediates hearing via repression of two neural targets.Genes Dev. 2023 Dec 26;37(21-24):1041-1051. doi: 10.1101/gad.351052.123. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 38110249 Free PMC article.
-
ELAV/Hu RNA binding proteins determine multiple programs of neural alternative splicing.PLoS Genet. 2021 Apr 7;17(4):e1009439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009439. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33826609 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cytological analysis of widely-used Gal4 driver lines for Drosophila neurobiology.BMC Genet. 2020 Oct 22;21(Suppl 1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12863-020-00895-7. BMC Genet. 2020. PMID: 33092520 Free PMC article.
-
A single-cell atlas of the sexually dimorphic Drosophila foreleg and its sensory organs during development.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jun 28;21(6):e3002148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002148. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37379332 Free PMC article.
-
Experience-dependent serotonergic signaling in glia regulates targeted synapse elimination.PLoS Biol. 2024 Oct 1;22(10):e3002822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002822. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39352884 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

