Bone Injury and Repair Trigger Central and Peripheral NPY Neuronal Pathways
- PMID: 27802308
- PMCID: PMC5089690
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165465
Bone Injury and Repair Trigger Central and Peripheral NPY Neuronal Pathways
Abstract
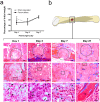
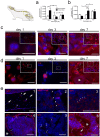
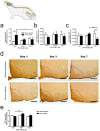
Bone repair is a specialized type of wound repair controlled by complex multi-factorial events. The nervous system is recognized as one of the key regulators of bone mass, thereby suggesting a role for neuronal pathways in bone homeostasis. However, in the context of bone injury and repair, little is known on the interplay between the nervous system and bone. Here, we addressed the neuropeptide Y (NPY) neuronal arm during the initial stages of bone repair encompassing the inflammatory response and ossification phases in femoral-defect mouse model. Spatial and temporal analysis of transcriptional and protein levels of NPY and its receptors, Y1R and Y2R, reported to be involved in bone homeostasis, was performed in bone, dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and hypothalamus after femoral injury. The results showed that NPY system activity is increased in a time- and space-dependent manner during bone repair. Y1R expression was trigged in both bone and DRG throughout the inflammatory phase, while a Y2R response was restricted to the hypothalamus and at a later stage, during the ossification step. Our results provide new insights into the involvement of NPY neuronal pathways in bone repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of neuropeptide Y and its receptors Y1 and Y2 in the rat heart and its supplying autonomic and spinal sensory ganglia in experimentally induced diabetes.Neuroscience. 2008 Feb 19;151(4):1016-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.07.069. Epub 2007 Dec 8. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18201831
-
A potential anti-allodynic mechanism of GDNF following L5 spinal nerve ligation; Mitigation of NPY up-regulation in the touch sense pathway.Neuroscience. 2015 Sep 24;304:240-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.059. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26215916
-
Characterization of neuropeptide Y2 receptor protein expression in the mouse brain. I. Distribution in cell bodies and nerve terminals.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Nov 20;499(3):357-90. doi: 10.1002/cne.21046. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16998904
-
Osteoblastic Actions of the Neuropeptide Y System to Regulate Bone and Energy Homeostasis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016 Feb;14(1):26-31. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0300-9. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016. PMID: 26872458 Review.
-
NPY regulation of bone remodelling.Neuropeptides. 2009 Dec;43(6):457-63. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.08.006. Epub 2009 Sep 11. Neuropeptides. 2009. PMID: 19748118 Review.
Cited by
-
A Pain That is Easily Overlooked: Referred Pain Caused by OVCF.J Pain Res. 2023 Mar 17;16:961-971. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S375966. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 36960463 Free PMC article.
-
Bone-nerve crosstalk: a new state for neuralizing bone tissue engineering-A mini review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 16;11:1386683. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1386683. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38690172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Early Life Stress on Bone Homeostasis in Mice and Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 10;21(18):6634. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186634. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32927845 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of action of neuropeptide Y on stem cells and its potential applications in orthopaedic disorders.World J Stem Cells. 2020 Sep 26;12(9):986-1000. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.986. World J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 33033559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropeptide Y1 receptor antagonist but not neuropeptide Y itself increased bone mineral density when locally injected with hyaluronic acid in male Wistar rats.Turk J Med Sci. 2020 Aug 26;50(5):1454-1460. doi: 10.3906/sag-2001-268. Turk J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32490636 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

