Major Neutrophilia Observed in Acute Phase of Human Leptospirosis Is Not Associated with Increased Expression of Granulocyte Cell Activation Markers
- PMID: 27802348
- PMCID: PMC5089758
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165716
Major Neutrophilia Observed in Acute Phase of Human Leptospirosis Is Not Associated with Increased Expression of Granulocyte Cell Activation Markers
Abstract
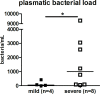
It has long been known that pathogenic Leptospira can mobilize the immune system but the specific contribution of neutrophils to control the infectious challenge remains to be clarified. We herein analyzed the phenotype of circulating neutrophils of patients with leptospirosis and healthy controls for the expression of toll-like receptor (TLR) type 2 (TLR2, to sense the leptospiral LPS) and several activation markers: interleukin 8 chemokine receptor CD182 (CXCR2), CD11b of the integrin/opsonin complement receptor type 3 (CR3) and CD15 (ligand of the selectin). The plasmatic level of the main CD182 ligand, interleukin 8 (CXCL8), was measured by ELISA. Hospitalized leptospirosis cases showed marked neutrophilia, particularly in the most severe cases. Interestingly, TLR2 was significantly increased in leptospirosis but identical levels of CD182 and CD11b were detected when compared to controls. CD15 was significantly decreased on neutrophils in leptospirosis but returned to normal within 1 month. Basal levels of IL-8 were measured in control subjects and were not increased in leptospirosis cases at the initial stage of the disease. In conclusion, we observed that neutrophils failed to regulate the expression of several of the receptors involved in cell activation and recruitment. This study further emphasizes the paradigm that neutrophils may be impaired in their overall capacity to thwart bacterial infection in leptospirosis patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Craig SB, Collet TA, Wynwood SJ, Smythe LD, Weier SL, McKay DB. Neutrophil counts in leptospirosis patients infected with different serovars. Trop Biomed. 2013;30: 579–583. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

