The prognostic performance of Adjuvant! Online and Nottingham Prognostic Index in young breast cancer patients
- PMID: 27802449
- PMCID: PMC5155359
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2016.359
The prognostic performance of Adjuvant! Online and Nottingham Prognostic Index in young breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Limited data are available on the prognostic performance of Adjuvant! Online (AOL) and Nottingham Prognostic Index (NPI) in young breast cancer patients.
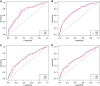
Methods: This multicentre hospital-based retrospective cohort study included young (⩽40 years) and older (55-60 years) breast cancer patients treated from January 2000 to December 2004 at four large Belgian and Italian institutions. Predicted 10-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) using AOL and 10-year OS using NPI were calculated for every patient. Tools ability to predict outcomes (i.e., calibration) and their discriminatory accuracy was assessed.
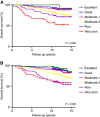
Results: The study included 1283 patients, 376 young and 907 older women. Adjuvant! Online accurately predicted 10-year OS (absolute difference: 0.7%; P=0.37) in young cohort, but overestimated 10-year DFS by 7.7% (P=0.003). In older cohort, AOL significantly underestimated both 10-year OS and DFS by 7.2% (P<0.001) and 3.2% (P=0.04), respectively. Nottingham Prognostic Index significantly underestimated 10-year OS in both young (8.5%; P<0.001) and older (4.0%; P<0.001) cohorts. Adjuvant! Online and NPI had comparable discriminatory accuracy.
Conclusions: In young breast cancer patients, AOL is a reliable tool in predicting OS at 10 years but not DFS, whereas the performance of NPI is sub-optimal.
Conflict of interest statement
HAA reports employment at Innate Pharma at the end of this study; this employment is not related in any sort to the subject of the current study. All the remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Azim HA Jr, Davidson NE, Ruddy KJ (2016) Challenges in Treating Premenopausal Women with Endocrine-Sensitive Breast Cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 35: 23–32. - PubMed
-
- Azim HA Jr, de Azambuja E, Colozza M, Bines J, Piccart MJ (2011) Long-term toxic effects of adjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Ann Oncol 22: 1939–1947. - PubMed
-
- Bhoo-Pathy N, Yip C-H, Hartman M, Saxena N, Taib NA, Ho G-F, Looi L-M, Bulgiba AM, van der Graaf Y, Verkooijen HM (2012) Adjuvant! Online is overoptimistic in predicting survival of Asian breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 48: 982–989. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

