Ion channels as insecticide targets
- PMID: 27802784
- PMCID: PMC6021766
- DOI: 10.1080/01677063.2016.1229781
Ion channels as insecticide targets
Abstract
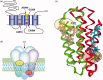
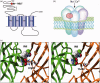
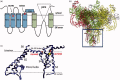
Ion channels remain the primary target of most of the small molecule insecticides. This review examines how the subunit composition of heterologously expressed receptors determines their insecticide-specific pharmacology and how the pharmacology of expressed receptors differs from those found in the insect nervous system. We find that the insecticide-specific pharmacology of some receptors, like that containing subunits of the Rdl encoded GABA receptor, can be reconstituted with very few of the naturally occurring subunits expressed. In contrast, workers have struggled even to express functional insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), and work has therefore often relied upon the expression of vertebrate receptor subunits in their place. We also examine the extent to which insecticide-resistance-associated mutations, such as those in the para encoded voltage-gated sodium channel, can reveal details of insecticide-binding sites and mode of action. In particular, we examine whether mutations are present in the insecticide-binding site and/or at sites that allosterically affect the drug preferred conformation of the receptor. We also discuss the ryanodine receptor as a target for the recently developed diamides. Finally, we examine the lethality of the genes encoding these receptor subunits and discuss how this might determine the degree of conservation of the resistance-associated mutations found.
Keywords: Drosophila; Insecticide resistance; ion channels.
Figures

References
-
- Bao W.X., Narai Y., Nakano A., Kaneda T., Murai T., & Sonoda S. (2014). Spinosad resistance of melon thrips, Thrips palmi, is conferred by G275E mutation in α6 subunit of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and cytochrome P450 detoxification. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 112, 51–55. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.04.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnard E.A., Bilbe G., Houamed K., Moss S.J., Van Renterghem C., & Smart T.G. (1987). Functional expression in the Xenopus oocyte of messenger ribonucleic acids encoding brain neurotransmitter receptors: Further characterisation of the implanted GABA receptor. Neuropharmacology, 26, 837–844. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(87)90060-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bass C., Puinean A.M., Andrews M., Cutler P., Daniels M., Elias J., …Slater R. et al. (2011). Mutation of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor β subunit is associated with resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides in the aphid Myzus persicae. BMC Neuroscience, 12, 51. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-12-51. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
