Combined sorafenib and yttrium-90 radioembolization for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27803608
- PMCID: PMC5081020
- DOI: 10.3747/co.23.2827
Combined sorafenib and yttrium-90 radioembolization for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background and aims: In this pilot study, we assessed the safety and tolerability of combining sorafenib with 90Y radioembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc).
Methods: The study, conducted prospectively during 2009-2012, included eligible patients with unresectable hcc and a life expectancy of at least 12 weeks. Each patient received sorafenib (400 mg twice daily) for 6-8 weeks before 90Y treatment. Safety and tolerability were assessed.
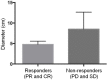
Results: Of the 40 patients enrolled, 29 completed treatment (combined therapy). In the initial cohort, the most common cause of hcc was hepatitis C (32.5%), and most patients were staged Child A (82.5%). The 29 patients who completed the study had similar baseline characteristics. Grades 1 and 2 toxicities accounted for 77.8% of all adverse events reported. The most common toxicities reported were fatigue (19.0%), alteration in liver function (7.9%), and diarrhea (6.3%). There were 12 grade 3 and 2 grade 4 toxicity events reported. One patient died of liver failure within 30 days after treatment. During the study, the sorafenib dose was reduced in 6 patients (20.7%), and sorafenib had to be interrupted in 4 patients (13.8%) and discontinued in 4 patients (13.8%). The disease control rate was 72.4% per the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, and tumour necrosis was observed in 82.8% of patients. Overall survival in patients undergoing combined therapy was 12.4 months.
Conclusions: Preliminary results demonstrate the safety and tolerability of combining 90Y radioembolization and sorafenib for advanced hcc. A larger prospective study is needed to determine the extent of the survival benefit.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; radioembolization; sorafenib; unresectability.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intra-Arterial TheraSphere Yttrium-90 Glass Microspheres in the Treatment of Patients With Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Protocol for the STOP-HCC Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2018 Aug 15;7(8):e11234. doi: 10.2196/11234. JMIR Res Protoc. 2018. PMID: 30111528 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and toxicity of radioembolization plus Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of the European multicentre trial SORAMIC.Liver Int. 2015 Feb;35(2):620-6. doi: 10.1111/liv.12622. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 24930619 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the survival and tolerability of radioembolization in elderly vs. younger patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):753-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.05.025. Epub 2013 May 23. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23707371 Clinical Trial.
-
Yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: what we know and what we need to know.Oncology. 2013;84 Suppl 1:34-9. doi: 10.1159/000345887. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Oncology. 2013. PMID: 23428856 Review.
-
Sorafenib for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncologist. 2009 Jan;14(1):95-100. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0185. Epub 2009 Jan 14. Oncologist. 2009. PMID: 19144678 Review.
Cited by
-
Radioembolization in the Setting of Systemic Therapies.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2021 Oct;38(4):472-478. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1735572. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34629716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-Arterial TheraSphere Yttrium-90 Glass Microspheres in the Treatment of Patients With Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Protocol for the STOP-HCC Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2018 Aug 15;7(8):e11234. doi: 10.2196/11234. JMIR Res Protoc. 2018. PMID: 30111528 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: hurdles, advances and prospects.Hepat Oncol. 2018 Sep 28;5(2):HEP08. doi: 10.2217/hep-2018-0002. eCollection 2018 Apr. Hepat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 31293776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signature of survival: a 18F-FDG PET based whole-liver radiomic analysis predicts survival after 90Y-TARE for hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 19;9(4):4549-4558. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23423. eCollection 2018 Jan 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29435123 Free PMC article.
-
Disease control and failure patterns of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma following transarterial radioembolization with yttrium-90 microspheres and with/without sorafenib.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Dec 21;27(47):8166-8181. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i47.8166. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 35068861 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

