Phase I Studies of Acebilustat: Biomarker Response and Safety in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 27806191
- PMCID: PMC5351012
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.12428
Phase I Studies of Acebilustat: Biomarker Response and Safety in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
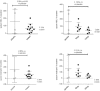
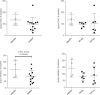
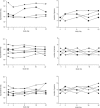
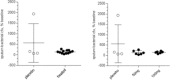
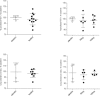
There is a significant unmet need for safe and effective anti-inflammatory treatment for cystic fibrosis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety of acebilustat, a leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor, and its effect on inflammation biomarkers in patients with cystic fibrosis. Seventeen patients with mild to moderate cystic fibrosis were enrolled and randomized into groups receiving placebo or doses of 50 mg or 100 mg acebilustat administered orally, once daily for 15 days. Sputum neutrophil counts were reduced by 65% over baseline values in patients treated with 100 mg acebilustat. A modestly significant 58% reduction vs. placebo in sputum elastase was observed with acebilustat treatment. Favorable trends were observed for reduction of serum C-reactive protein and sputum neutrophil DNA in acebilustat-treated patients. No changes in pulmonary function were observed. Acebilustat was safe and well tolerated. The results of this study support further clinical development of acebilustat for treatment of cystic fibrosis.
© 2016 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Lethem, M.I. , James, S.L. , Marriott, C. & Burke, J.F. The origin of DNA associated with mucus glycoproteins in cystic fibrosis sputum. Eur. Respir. J. 3, 19–23(1990). - PubMed
-
- Chua, F. & Laurent, G.J. Neutrophil elastase: mediator of extracellular matrix destruction and accumulation. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 3, 424–427 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kelly, E. , Greene, C.M. & McElvaney, N.G. Targeting neutrophil elastase in cystic fibrosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 12, 145–157 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

