Characteristics of gram-negative urinary tract infections caused by extended spectrum beta lactamases: pivmecillinam as a treatment option within South Dublin, Ireland
- PMID: 27806687
- PMCID: PMC5093942
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-016-1797-3
Characteristics of gram-negative urinary tract infections caused by extended spectrum beta lactamases: pivmecillinam as a treatment option within South Dublin, Ireland
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae is increasing and the therapeutic options are limited, especially in primary care. Recent indications have suggested pivmecillinam to be a suitable option. This pilot study aimed to assess the viability of pivmecillinam as a therapeutic option in a Dublin cohort of mixed community and healthcare origin.
Methods: A prospective measurement of mean and fractional inhibitory concentrations of antibiotic use in 95 patients diagnosed with UTI caused by ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae was carried out. 36 % patients were from general practice, 40 % were admitted to hospital within south Dublin, and 25 % samples arose from nursing homes. EUCAST breakpoints were used to determine if an isolate was sensitive or resistant to antibiotic agents.
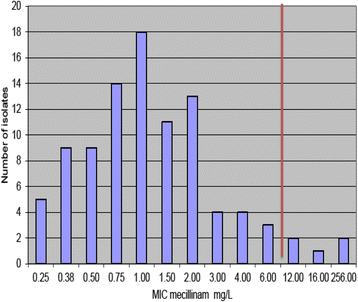
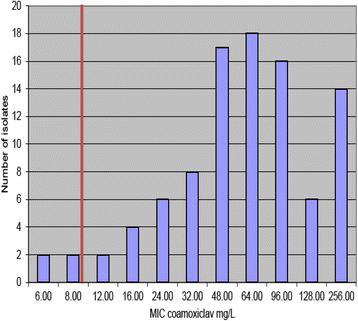
Results: Sixty-nine percent of patients (N = 66) with urinary ESBL isolates were female. The mean age of females was 66 years compared with a mean age of 74 years for males. Thirty-six percent of isolates originated from primary care, hospital inpatients (26 %), and nursing homes (24 %). The vast majority of ESBL isolates were E. coli (80 %). The E tests for mecillinam and co-amoxiclav had concentration ranges from 0.16 mg/L up to 256 mg/L. The mean inhibitory concentration (MIC) of mecillinam ranged from 0.25 to 256 mg/L, while co-amoxiclav MICs ranged from 6 to 256 mg/L. The percentage of isolates resistant to mecillinam and co-amoxiclav was found to be 5.26 and 94.74 % respectively.
Conclusions: This is the first study exploring the use of pivmecillinam in an Irish cohort and has demonstrated that its use in conjunction with or without co-amoxiclav is an appropriate and useful treatment for urinary tract infections caused by ESBL-producing organisms.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Escherichia coli; Extended-spectrum beta lactamase; Mean inhibitory concentration; Pivmecillinam; Urinary tract infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and bacteriological effects of pivmecillinam for ESBL-producing Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae in urinary tract infections.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Mar;69(3):769-72. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt404. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24107388
-
Emerging clinical role of pivmecillinam in the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by Extended Spectrum βeta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacteriaceae.Int J Clin Pract. 2019 Sep;73(9):1-5. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.13387. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Int J Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31243859
-
Efficacy of pivmecillinam for treatment of lower urinary tract infection caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.Microb Drug Resist. 2012 Apr;18(2):189-92. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2011.0161. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Microb Drug Resist. 2012. PMID: 22204597 Clinical Trial.
-
New Perspectives on Antimicrobial Agents: Pivmecillinam.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Aug 6;69(8):e0182424. doi: 10.1128/aac.01824-24. Epub 2025 Jul 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40689785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria causing urinary tract infections: a review.J Chemother. 2017 Dec;29(sup1):2-9. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2017.1380395. J Chemother. 2017. PMID: 29271736 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and food-effect of pivmecillinam after single- and multiple-dose in healthy Chinese subjects: a phase I study.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7639-7647. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03118-3. Epub 2024 May 1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38691150 Clinical Trial.
-
Mecillinam for the treatment of acute pyelonephritis and bacteremia caused by Enterobacteriaceae: a literature review.Infect Drug Resist. 2018 May 24;11:761-771. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S163280. eCollection 2018. Infect Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29872326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of the In Vitro Microbiological Activity of Mecillinam Against Common Uropathogens in Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection: Focus on Resistant Pathogens.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 May 24;11(6):ofae296. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae296. eCollection 2024 Jun. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38868308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

