Doxycycline in early CJD: a double-blinded randomised phase II and observational study
- PMID: 27807198
- PMCID: PMC5284486
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-313541
Doxycycline in early CJD: a double-blinded randomised phase II and observational study
Abstract
Objectives: The main objective of the present study is to study the therapeutic efficiency of doxycycline in a double-blinded randomised phase II study in a cohort of patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD).
Methods: From the National Reference Center of TSE Surveillance in Germany, patients with probable or definite sCJD were recruited for a double-blinded randomised study with oral doxycycline (EudraCT 2006-003934-14). In addition, we analysed the data from patients with CJD who received compassionate treatment with doxycycline in a separate group. Potential factors which influence survival such as age at onset, gender, codon 129 polymorphism and cognitive functions were evaluated. The primary outcome measure was survival.
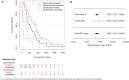
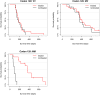
Results: Group 1: in the double-blinded randomised phase II study, 7 patients in the treatment group were compared with 5 controls. Group 2: 55 patients with sCJD treated with oral doxycycline were analysed and compared with 33 controls by a stratified propensity score applied to a Cox proportional hazard analysis. The results of both studies were combined by means of a random-effects meta-analysis. A slight increase in survival time in the doxycycline treatment group was observed (p=0.049, HR=0.63 (95% CI 0.402 to 0.999)).
Conclusions: On the basis of our studies, a larger trial of doxycycline should be performed in persons in the earliest stages of CJD.
Trial registration number: EudraCT 2006-003934-14; Results.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Association between naturally occurring antiamyloid β autoantibodies and medial temporal lobe atrophy in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017 Feb;88(2):96-97. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-314136. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27486155 No abstract available.
-
Many challenges of conducting clinical trials in CJD.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017 Feb;88(2):98. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-314578. Epub 2016 Nov 4. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27815323 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
