Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Moringa oleifera in Downregulating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages
- PMID: 27809259
- PMCID: PMC6273666
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21111452
Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Moringa oleifera in Downregulating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages
Abstract
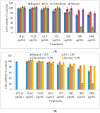
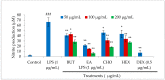
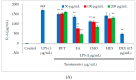
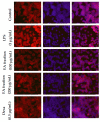
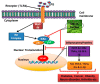
In the present investigation, we prepared four different solvent fractions (chloroform, hexane, butanol, and ethyl acetate) of Moringa oleifera extract to evaluate its anti-inflammatory potential and cellular mechanism of action in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW264.7 cells. Cell cytotoxicity assay suggested that the solvent fractions were not cytotoxic to macrophages at concentrations up to 200 µg/mL. The ethyl acetate fraction suppressed LPS-induced production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages in a concentration-dependent manner and was more effective than the other fractions. Immunoblot observations revealed that the ethyl acetate fraction effectively inhibited the expression of inflammatory mediators including cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65 through suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Furthermore, it upregulated the expression of the inhibitor of κB (IκBα) and blocked the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. These findings indicated that the ethyl acetate fraction of M. oleifera exhibited potent anti-inflammatory activity in LPS-stimulated macrophages via suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: IκBα; RAW264.7 cells; inflammation; inflammatory mediators; proinflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ueda F., Iizuka K., Tago K., Narukawa Y., Kiuchi F., Kasahara T., Tamura H., Funakoshi-Tago M. Nepetaefuran and leonotinin isolated from leonotis nepetaefolia R. Br. Potently inhibit the LPS signaling pathway by suppressing the transactivation of NF-κB. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015;28:967–976. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.08.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vo V.A., Lee J.-W., Shin S.-Y., Kwon J.-H., Lee H.J., Kim S.-S., Kwon Y.-S., Chun W. Methyl p-hydroxycinnamate suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through akt phosphorylation in RAW264.7 cells. Biomol. Ther. 2014;22:10–16. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2013.095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

