Immunohistochemistry for Pathologists: Protocols, Pitfalls, and Tips
- PMID: 27809448
- PMCID: PMC5122731
- DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2016.08.08
Immunohistochemistry for Pathologists: Protocols, Pitfalls, and Tips
Abstract
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is an important auxiliary method for pathologists in routine diagnostic work as well as in basic and clinical research including exploration of biomarkers, as IHC allows confirmation of target molecule expressions in the context of microenvironment. Although there has been a considerable progress in automation and standardization of IHC, there are still many things to be considered in proper optimization and appropriate interpretation. In this review, we aim to provide possible pitfalls and useful tips for practicing pathologists and residents in pathology training. First, general procedure of IHC is summarized, followed by pitfalls and tips in each step and a summary of troubleshooting. Second, ways to an accurate interpretation of IHC are discussed, with introduction to general quantification and analysis methods. This review is not intended to provide complete information on IHC, but to be used as a basic reference for practice and publication.
Keywords: Antigen-antibody reactions; Auxiliary test; Immmunohistochemistry; Immunostain.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
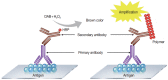
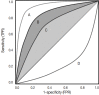
References
-
- Schacht V, Kern JS. Basics of immunohistochemistry. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:e30 - PubMed
-
- Gustavson MD, Bourke-Martin B, Reilly D, et al. Standardization of HER2 immunohistochemistry in breast cancer by automated quantitative analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:1413–9. - PubMed
-
- Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N. Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2005.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

