Failure of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in a traveller coming from Ethiopia
- PMID: 27809844
- PMCID: PMC5094029
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-016-1572-3
Failure of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in a traveller coming from Ethiopia
Abstract
Background: Artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) is used worldwide as the first-line treatment against uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Despite the success of ACT in reducing the global burden of malaria, the emerging of resistance to artemisinin threatens its use.
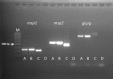
Case report: This report describes the first case of failure of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine (DHA-PPQ) for the treatment of P. falciparum malaria diagnosed in Europe. It occurred in an Italian tourist returned from Ethiopia. She completely recovered after the DHA-PPQ treatment but 32 days after the end of therapy she had a recrudescence. The retrospective analysis indicated a correct DHA-PPQ absorption and genotyping demonstrated that the same P. falciparum strain was responsible for the both episodes.
Conclusion: In consideration of the growing number of cases of resistance to ACT, it is important to consider a possible recrudescence, that can manifest also several weeks after treatment.
Keywords: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine (DHA-PPQ); Failure; Plasmodium falciparum; Recrudescence.
Figures
References
-
- Pfeil J, Borrmann S, Bassat Q, Mulenga M, Talisuna A, Tozan Y. An economic evaluation of the posttreatment prophylactic effect of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine for first-line treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria across different transmission settings in Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93:961–966. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources