Comparative effects of nebivolol and carvedilol on left ventricular diastolic function in older heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 27809882
- PMCID: PMC5093969
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1656-y
Comparative effects of nebivolol and carvedilol on left ventricular diastolic function in older heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is a common and disabling condition in older people. Randomized clinical trials and meta-analyses have clearly demonstrated that the long-term use of β-Blockers improves the outcome of patients with HF. However, limited data are available on the treatment of older HF patients with preserved ejection fraction (EF). No study has specifically compared the relative effectiveness of carvedilol and nebivolol in treating HF in older patients with preserved EF.
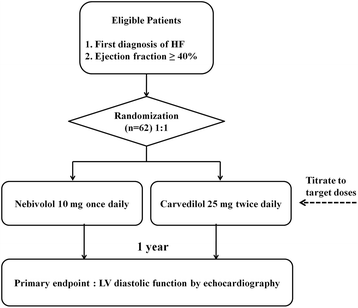
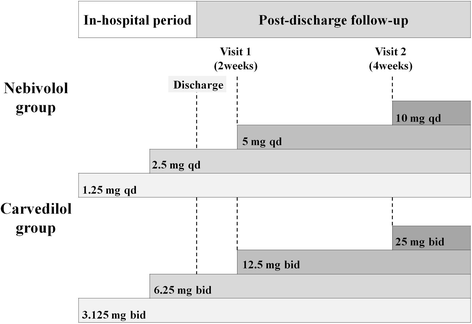
Method/design: This trial is a prospective, randomized, open-label, single-centre, active controlled study designed to investigate the effects of nebivolol and carvedilol on diastolic function of the left ventricle (LV) in older HF patients with preserved EF. We will test the hypothesis that nebivolol improves LV diastolic function to a greater extent than carvedilol in patients over 70 years of age. The study population includes 62 older patients newly diagnosed with HF. Patients will be included in the study if they have a LVEF ≥40 %, New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classes I, II or III status, and have been clinically stable without hospital admission for HF in the preceding 3 months. Eligible patients will be randomly assigned, in a 1:1 ratio, to receive a loading and maintenance dose of either nebivolol or carvedilol. Echocardiographic evaluations will be performed at baseline, 6, and 12 months after therapy. Clinical assessment and laboratory tests are to be performed at fixed times.
Discussion: This trial is a single-center study that aims to evaluate the impact of nebivolol on LV diastolic function. The results of the study will provide information about the optimal choice of a β-Blocker in the management of patients after diagnosis of HF with preserved EF. The results will be available by 2017.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02619526 , registered on 25 November 2015.
Keywords: Carvedilol; Heart failure; Nebivolol.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous