HbA1c and the Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adults
- PMID: 27810987
- PMCID: PMC5180461
- DOI: 10.2337/dc16-1358
HbA1c and the Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adults
Abstract
Objective: Long-term data validating glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in assessing the risk of type 2 diabetes in children are limited. HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-h postload plasma glucose (2hPG) concentrations were measured in a longitudinal study of American Indians to determine their utility in predicting incident diabetes, all of which is thought to be type 2 in this population.
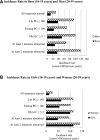
Research design and methods: Incident diabetes (FPG ≥126 mg/dL [7.0 mmol/L], 2hPG ≥200 mg/dL [11.1 mmol/L], HbA1c ≥6.5% [8 mmol/mol], or clinical diagnosis) was determined in 2,095 children without diabetes ages 10-19 years monitored through age 39, and in 2,005 adults ages 20-39 monitored through age 59. Areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for HbA1c, FPG, and 2hPG in predicting diabetes within 10 years were compared.
Results: During long-term follow-up of children and adolescents who did not initially have diabetes, the incidence rate of subsequent diabetes was fourfold (in boys) as high and more than sevenfold (in girls) as high in those with HbA1c ≥5.7% as in those with HbA1c ≤5.3%-greater rate ratios than experienced by adults in the same HbA1c categories. Analyses of ROCs revealed no significant differences between HbA1c, FPG, and 2hPG in sensitivity and specificity for identifying children and adolescents who later developed diabetes.
Conclusions: HbA1c is a useful predictor of diabetes risk in children and can be used to identify prediabetes in children with other type 2 diabetes risk factors with the same predictive value as FPG and 2hPG.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
-
- Rodriguez BL, Fujimoto WY, Mayer-Davis EJ, et al. . Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors in U.S. children and adolescents with diabetes: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1891–1896 - PubMed
-
- Kershnar AK, Daniels SR, Imperatore G, et al. . Lipid abnormalities are prevalent in youth with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. J Pediatr 2006;149:314–319 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

