Cathelicidin Insufficiency in Patients with Fatal Leptospirosis
- PMID: 27812211
- PMCID: PMC5094754
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005943
Cathelicidin Insufficiency in Patients with Fatal Leptospirosis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Cathelicidin Insufficiency in Patients with Fatal Leptospirosis.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Sep 26;13(9):e1006646. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006646. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28950012 Free PMC article.
Abstract
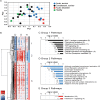
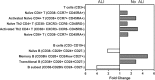
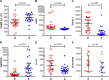
Leptospirosis causes significant morbidity and mortality worldwide; however, the role of the host immune response in disease progression and high case fatality (>10-50%) is poorly understood. We conducted a multi-parameter investigation of patients with acute leptospirosis to identify mechanisms associated with case fatality. Whole blood transcriptional profiling of 16 hospitalized Brazilian patients with acute leptospirosis (13 survivors, 3 deceased) revealed fatal cases had lower expression of the antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin, and chemokines, but more abundant pro-inflammatory cytokine receptors. In contrast, survivors generated strong adaptive immune signatures, including transcripts relevant to antigen presentation and immunoglobulin production. In an independent cohort (23 survivors, 22 deceased), fatal cases had higher bacterial loads (P = 0.0004) and lower anti-Leptospira antibody titers (P = 0.02) at the time of hospitalization, independent of the duration of illness. Low serum cathelicidin and RANTES levels during acute illness were independent risk factors for higher bacterial loads (P = 0.005) and death (P = 0.04), respectively. To investigate the mechanism of cathelicidin in patients surviving acute disease, we administered LL-37, the active peptide of cathelicidin, in a hamster model of lethal leptospirosis and found it significantly decreased bacterial loads and increased survival. Our findings indicate that the host immune response plays a central role in severe leptospirosis disease progression. While drawn from a limited study size, significant conclusions include that poor clinical outcomes are associated with high systemic bacterial loads, and a decreased antibody response. Furthermore, our data identified a key role for the antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin, in mounting an effective bactericidal response against the pathogen, which represents a valuable new therapeutic approach for leptospirosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Torgerson PR, Hagan JE, Costa F, Calcagno J, Kane M, Martinez-Silveira MS, et al. Global Burden of Leptospirosis: Estimated in Terms of Disability Adjusted Life Years. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2015;9(10):e0004122 PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4591975. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004122 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leptospirosis case notification records, Brazil: Health Surveillance Secretary Brazilian Ministry of Health; 2007.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

