Therapeutic role of axillary lymph node dissection in patients with stage IV breast cancer: a population-based analysis
- PMID: 27812853
- PMCID: PMC11819261
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-016-2295-0
Therapeutic role of axillary lymph node dissection in patients with stage IV breast cancer: a population-based analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the clinical value of axillary lymph node (ALN) dissection in stage IV breast cancer.
Methods: Patients with a diagnosis of stage IV breast cancer from 1990 to 2010 were identified using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to analyze the effect of ALN dissection and ALN status on breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) and overall survival (OS).
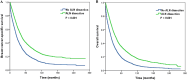
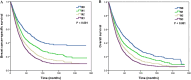
Results: A total of 11,645 patients were identified. Of these, 7358 (63.2%) patients underwent ALN dissection, and 6168 (83.8%) patients showed nodal positivity. During this time, the rate of ALN dissection increased. Patients with delayed diagnosis, age <50 years, poorly/undifferentiated disease, larger tumor size (>2 cm), and married women were more likely to undergo ALN dissection. ALN dissection was associated with improved BCSS and OS in multivariate analysis. ALN dissection improved the survival in patients with bone and liver metastasis, and patients with single site of distant metastasis also had survival benefit by ALN dissection. Lymph node staging based on the number of positive lymph nodes was the independent prognostic factor for BCSS and OS in multivariate analysis; patients with advanced lymph node staging had a poor survival.
Conclusions: ALN dissection may improve survival in patients with stage IV breast cancer who received primary tumor surgery, especially in patients with bone, liver, and single site of distant metastasis. The lymph node staging was also the prognostic factor in patients with stage IV breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Lymph node dissection; Metastatic; SEER; Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Babiera GV, Rao R, Feng L, Meric-Bernstam F, Kuerer HM, Singletary SE, Hunt KK, Ross MI, Gwyn KM, Feig BW, Ames FC, Hortobagyi GN (2006) Effect of primary tumor extirpation in breast cancer patients who present with stage IV disease and an intact primary tumor. Ann Surg Oncol 13(6):776–782 - PubMed
-
- Badwe R, Hawaldar R, Nair N, Kaushik R, Parmar V, Siddique S, Budrukkar A, Mittra I, Gupta S (2015) Locoregional treatment versus no treatment of the primary tumour in metastatic breast cancer: an open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 16(13):1380–1388 - PubMed
-
- Blanchard DK, Shetty PB, Hilsenbeck SG, Elledge RM (2008) Association of surgery with improved survival in stage IV breast cancer patients. Ann Surg 247(5):732–738 - PubMed
-
- Cardoso F, Costa A, Norton L, Senkus E, Aapro M, André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Biganzoli L, Blackwell KL, Cardoso MJ, Cufer T, El Saghir N, Fallowfield L, Fenech D, Francis P, Gelmon K, Giordano SH, Gligorov J, Goldhirsch A, Harbeck N, Houssami N, Hudis C, Kaufman B, Krop I, Kyriakides S, Lin UN, Mayer M, Merjaver SD, Nordström EB, Pagani O, Partridge A, Penault-Llorca F, Piccart MJ, Rugo H, Sledge G, Thomssen C, Van’t Veer L, Vorobiof D, Vrieling C, West N, Xu B, Winer E, European School of Oncology, European Society of Medical Oncology (2014) ESO-ESMO 2nd international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC2). Breast 23(5):489–502 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

