Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity
- PMID: 27814509
- PMCID: PMC5131922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.020
Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity
Erratum in
-
ALKBH1-Mediated tRNA Demethylation Regulates Translation.Cell. 2016 Dec 15;167(7):1897. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.045. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27984735 No abstract available.
-
Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity.Cell. 2016 Dec 15;167(7):1897. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.046. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27984736 No abstract available.
Abstract
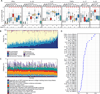
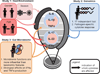
Gut microbial dysbioses are linked to aberrant immune responses, which are often accompanied by abnormal production of inflammatory cytokines. As part of the Human Functional Genomics Project (HFGP), we investigate how differences in composition and function of gut microbial communities may contribute to inter-individual variation in cytokine responses to microbial stimulations in healthy humans. We observe microbiome-cytokine interaction patterns that are stimulus specific, cytokine specific, and cytokine and stimulus specific. Validation of two predicted host-microbial interactions reveal that TNFα and IFNγ production are associated with specific microbial metabolic pathways: palmitoleic acid metabolism and tryptophan degradation to tryptophol. Besides providing a resource of predicted microbially derived mediators that influence immune phenotypes in response to common microorganisms, these data can help to define principles for understanding disease susceptibility. The three HFGP studies presented in this issue lay the groundwork for further studies aimed at understanding the interplay between microbial, genetic, and environmental factors in the regulation of the immune response in humans. PAPERCLIP.
Keywords: Human Functional Genomics Project; database of microbiome-cytokine associations; healthy human cohort; human gut microbiome; immunological profiles; inflammatory cytokine response; interindividual variation; metagenomics; microbial profiles; microbiome-host interactions.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Oshima K, Suda W, Nagano Y, Nishikawa H, Fukuda S, Saito T, Narushima S, Hase K, et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature. 2013;500:232–236. - PubMed
-
- Bronte V, Zanovello P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005;5:641–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

